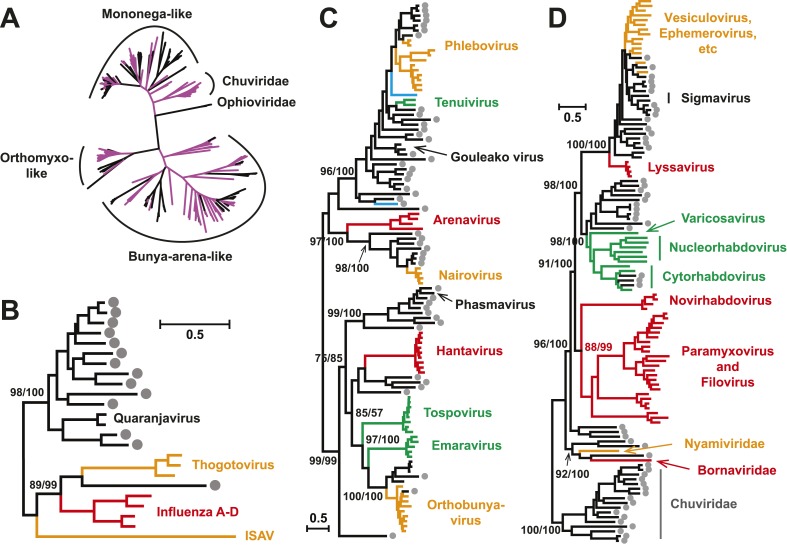
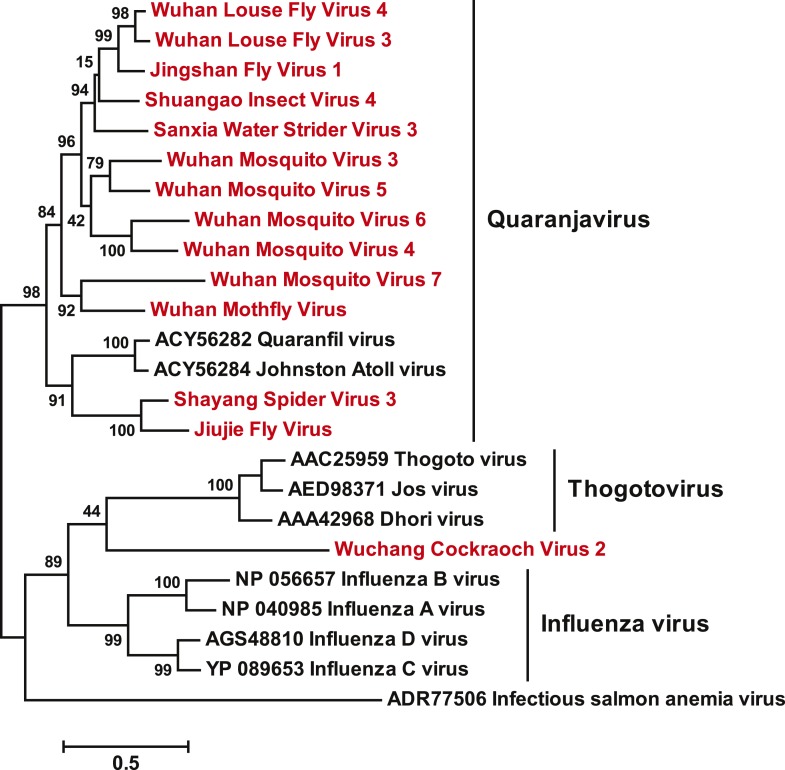
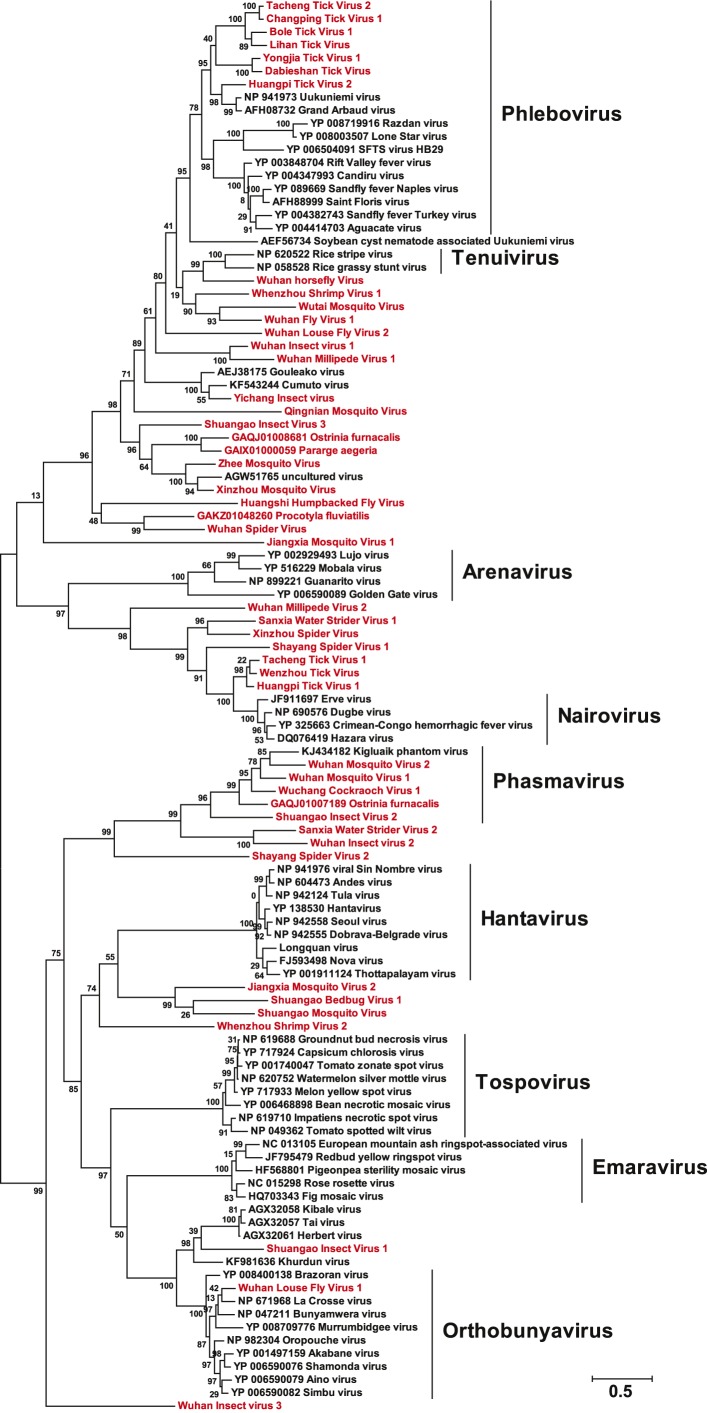
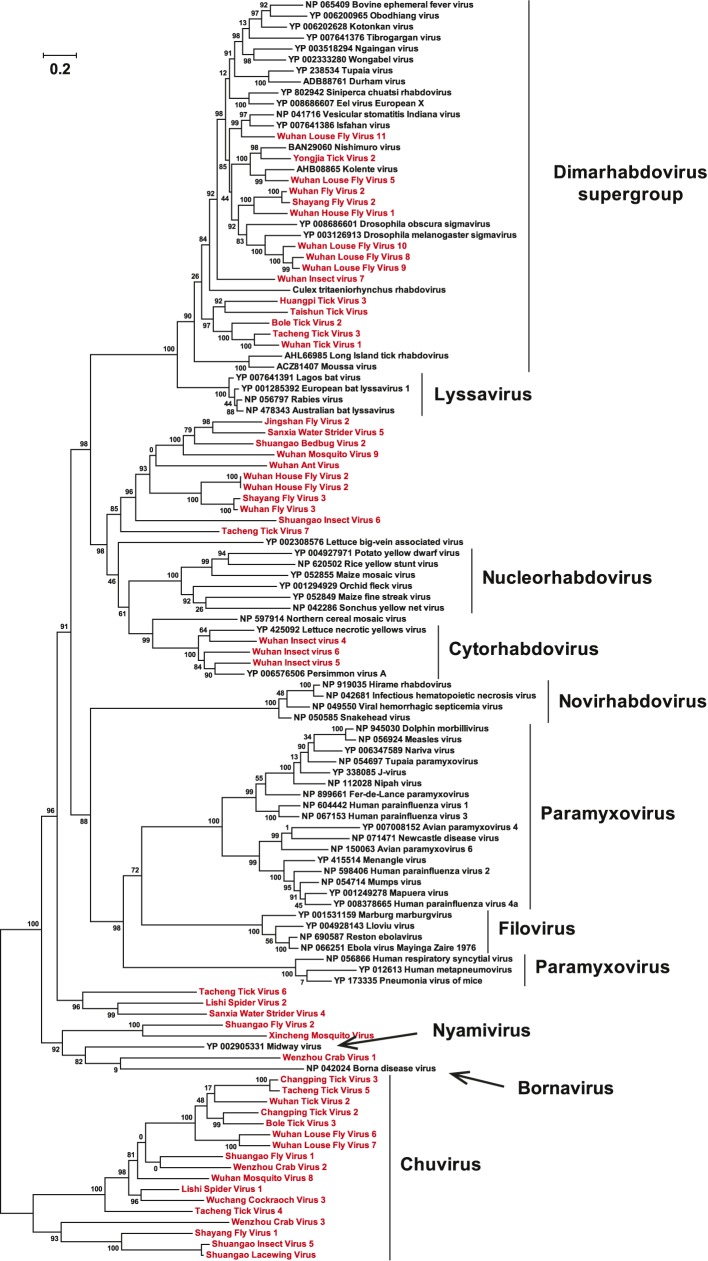
Figure 3. Evolutionary history of negative-sense RNA viruses based on RdRp.
This is initially displayed in an unrooted maximum likelihood (ML) tree including all major groups of negative-sense RNA viruses (A). Separate and more detailed ML phylogenies are then shown for the Orthomyxoviridae-like (B), Bunya-Arenaviridae-like (C), and Mononegavirales-like viruses (D). In all the phylogenies, the RdRp sequences described here from arthropods are either shaded purple or marked with solid gray circles. The names of previously defined genera/families are labeled to the right of the phylogenies. Based on their host types, the branches are shaded red (vertebrate-specific), yellow (vertebrate and arthropod), green (plant and arthropod), blue (non-arthropod invertebrates), or black (arthropod only). For clarity, statistical supports (i.e., approximate likelihood-ratio test (aLRT) with Shimodaira–Hasegawa-like procedure/posterior probabilities) are shown for key internal nodes only.