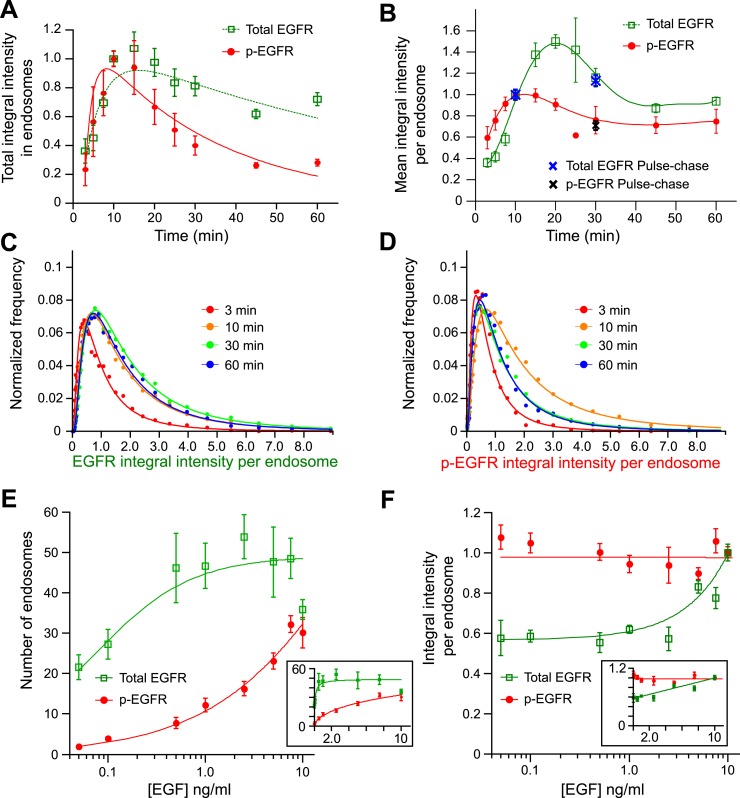
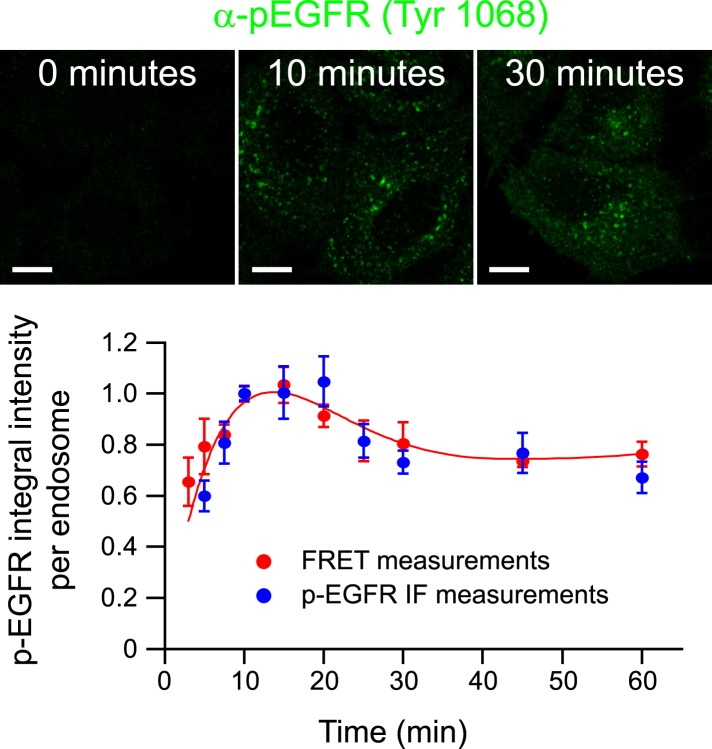
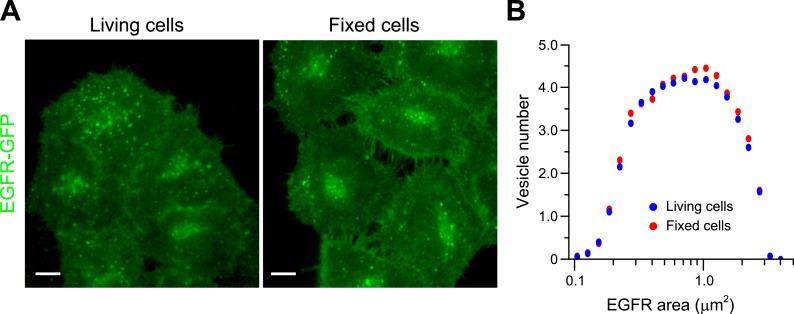
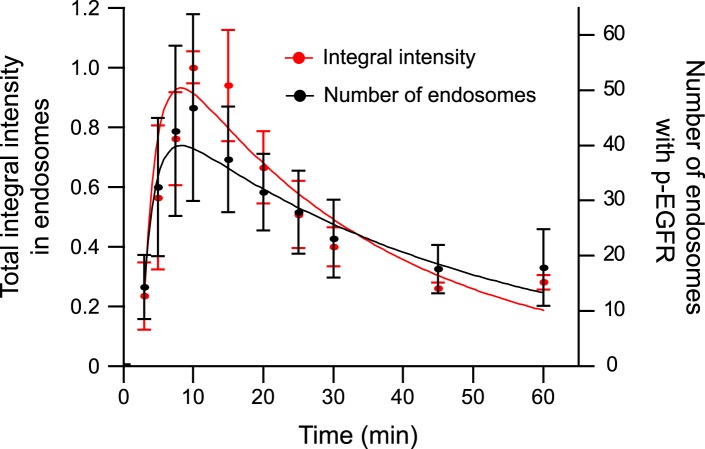
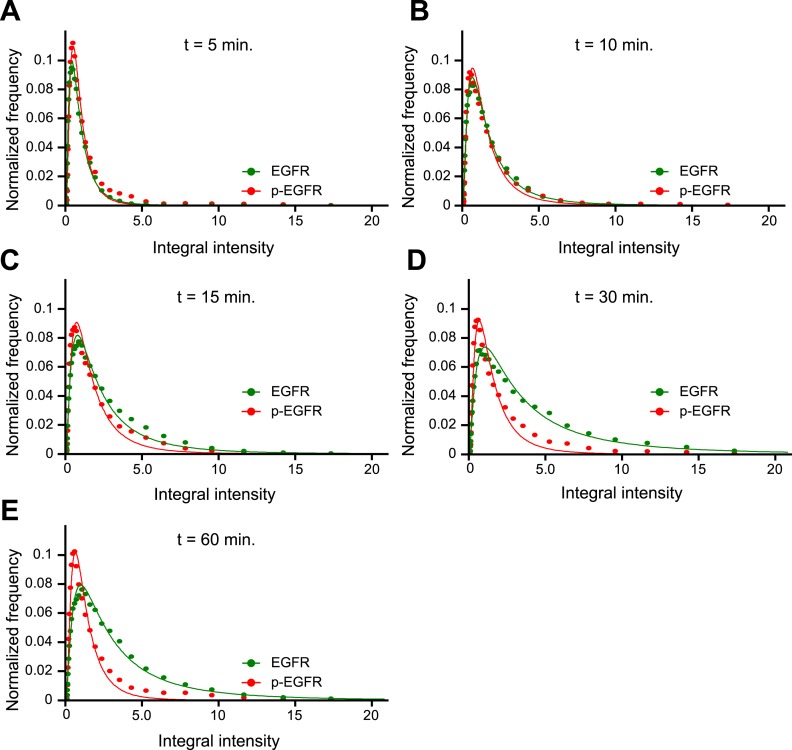
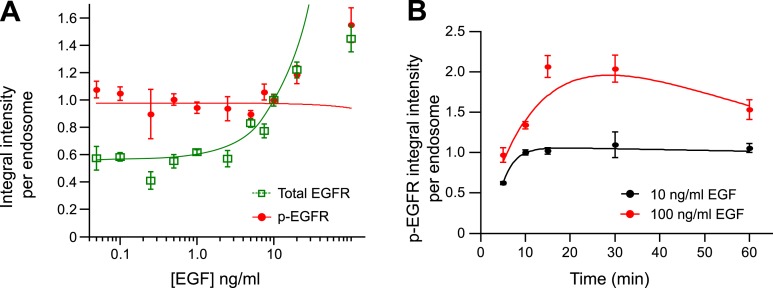
Figure 1. Cells keep a constant amount of p-EGFR in endosomes.
(A) Time course of total integral intensity of EGFR (green) and p-EGFR (red) in endosomes measured by a FRET microscopy assay in HeLa EGFR BAC cells after continuous stimulation with 10 ng/ml EGF. The total integral intensity is defined as the sum of integral intensities of all endosomes in an image normalized by the area covered by the cells (for details see ‘Materials and methods’ and Supplementary information). (B) Time course of mean integral intensity per endosome for total EGFR (green curve) and p-EGFR (red curve) as in (A). Intensity curves (A–B) were normalized to the intensity value at 10 min. Crosses show the corresponding values after 1 min of EGF stimulation and incubation in ligand-free medium for 10 or 30 min (pulse-chase). (C) Time course of histogram distributions of the total EGFR integral intensity per endosome upon EGF stimulation as in (A). (D) Time course of histogram distributions of the p-EGFR integral intensity per endosome upon EGF stimulation as in (A). In both graphs, receptors in CCVs are responsible for the width of the distribution at 3 min (red curves in C and D). For comparison, histogram amplitude in B and C were normalized by each curve integral. In each graph, the integral intensity values were scaled by the mode of the histogram at 10 min. The experimental points from all histograms were fitted with a log-normal distribution. (E–F) Distribution of p-EGFR in endosomes as a function of EGF concentration after continuous stimulation for 30 min. Mean number of endosomes with EGFR (green curve) and p-EGFR (red curve) per 1000 μm2 of the area covered by cells (E) and mean integral intensity of EGFR (green curve) and p-EGFR (red curve) per endosome (F). On panel (F) curves were normalized to the intensity value at 10 ng/ml EGF. Lines are hyperbolic fits (E) or least square fits (F) to the experimental points. In both cases insets show the same graphs in linear scale. The different magnitude of the error bars in (E) and (F) is due to the averaging by the total number of images (E) or the total number of endosomes (F). In all cases, points show mean ± SEM. All measurements were done in three independent experiments with a total of ∼150 cells per time point or condition.