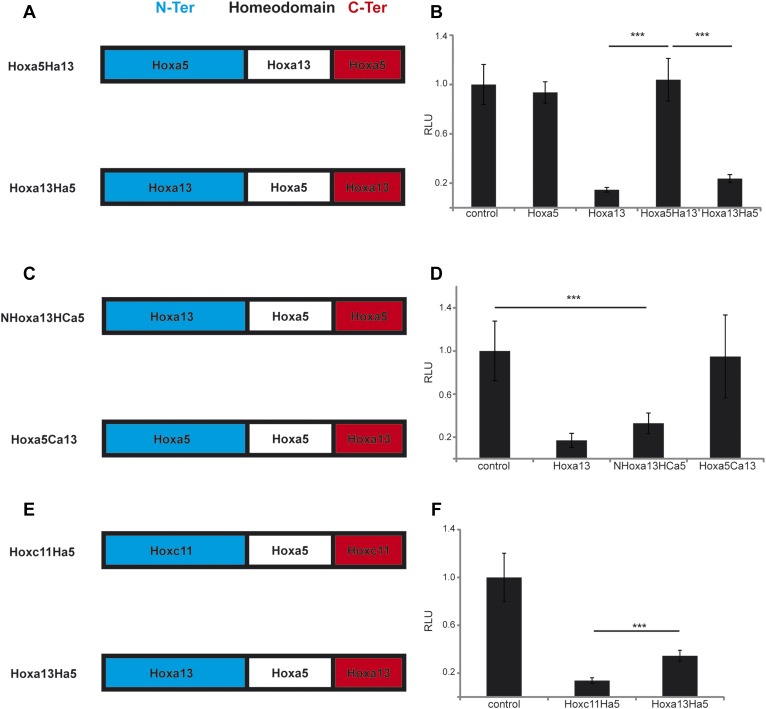
Figure 10. The N-terminal region of posterior Hox genes contains the repressive domain.
(A, C, E) Design of the Hox chimeras. N-ter is in blue, the homeodomain in white, and the C-ter in red. (B, D, F) Luciferase assay measuring T/brachyury expression 20 hr after over-expression of cTprLuc and Renilla constructs together with (B) control, Hoxa5, Hoxa13, Hoxa5Ha13, or Hoxa13Ha5, (D) control, Hoxa13, NHox13HCa5, or Hoxa5Ca13, (E) control, Hoxc11Ha5, or Hoxa13Ha5. Stars represent the p-value of the two-tailed Student's t-test applied between the different conditions. ***p < 0.005. Error bars represent the standard error to the mean (SEM).