Figure 5.
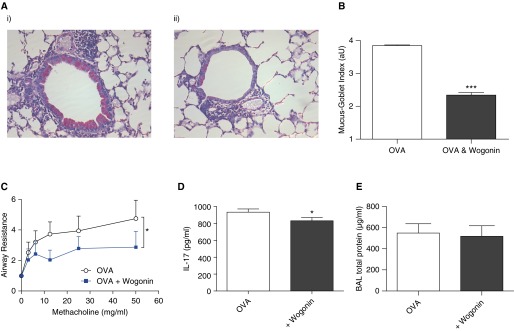
Wogonin improves allergic airway responses. Following ovalbumin (OVA) sensitization and challenges, mice were treated with wogonin (1 mg) or vehicle control on Days 25–28, with acquisition and analysis of tissue and lung function performed on Day 29. (A) Representative lung tissue sections stained with periodic acid–Schiff stain in (i) OVA- and (ii) OVA- and wogonin-treated animals (×200 original magnification). (B) Quantification of mucus production was assessed by the mucus-goblet index, an average severity score per airway, expressed in arbitrary units (aU) (n = 4 or 5 mice per group). (C) Airway responsiveness was assessed in anesthetized and mechanically ventilated mice in response to aerosolized methacholine, with lung resistance determined and expressed relative to baseline values after phosphate-buffered saline exposure. (D) Lung IL-17 concentration and (E) bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) protein (n ≥ 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM as analyzed by two-way analysis of variance (C) or unpaired t test (B, D, and E). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 versus control.
