Figure 1.
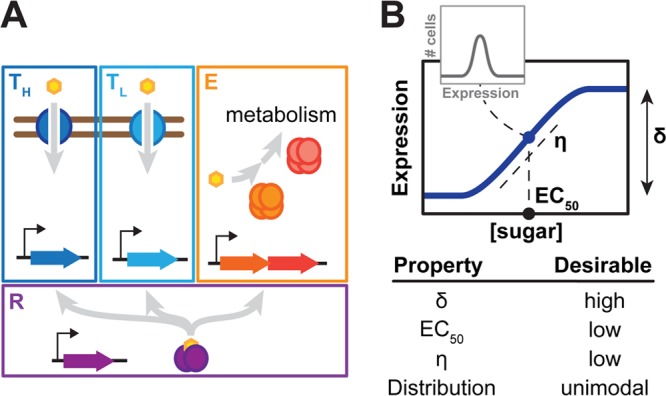
Co-opting sugar utilization pathways for titratable control of gene expression. (A) Components of inducible sugar utilization pathways. High affinity (TH) and low-affinity (TL) transporters import the sugar into the cell, while catabolic enzymes (E) shunt the sugar into central metabolism. Transcription regulators (R) up-regulate the expression of the transporters and the enzymes, but only in the presence of the sugar. (B) Desirable properties for a titratable response. These properties include a uniform response at all inducer concentrations, a large dynamic range (high δ), low inducer concentrations to induce the pathway (low EC50), and strong linearity (low η).
