Fig. 1. Gln, but not Leu, activates mTORC1 independently of RagA and RagB.
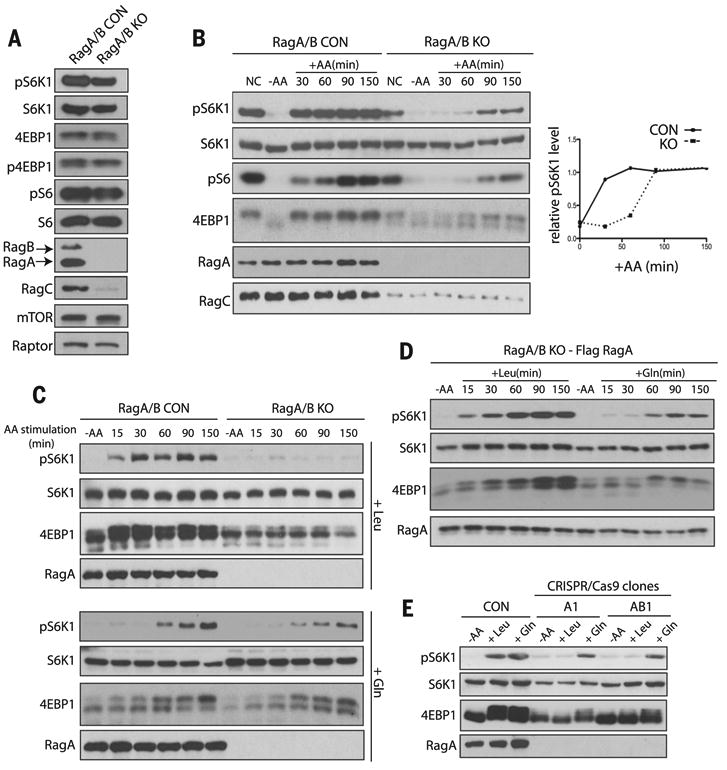
mTORC1 activity was analyzed by the phosphorylation of S6K1 (pS6K1), S6 (pS6), and 4EBP1 (p4EBP1) and the mobility shift of 4EBP1. AA, amino acids. (A) mTORC1 activity was analyzed in control (CON) and RagA/B KO MEFs under normal conditions (NC). mTOR, Raptor, RagA, RagB, and RagC protein were also analyzed. (B) mTORC1 activity was analyzed in CON and RagA/B KO MEFs under NC, in the absence of amino acids (–AA) and at the indicated times after the addition of amino acids (+AA) (left). Relative abundance of pS6K1 is plotted (right). (C) mTORC1 activity after stimulation with Leu (top) or Gln (bottom) in CON and RagA/B KO MEFs. (D) mTORC1 activity was analyzed after stimulation with Leu or Gln in RagA/B KO MEFs stably expressing Flag-tagged RagA at the indicated times. (E) mTORC1 activity was analyzed in CON, RagA KO (A1) and RagA/B KO (AB1) HEK293A cells that were starved of amino acids or stimulated with Leu or Gln for 150 min.
