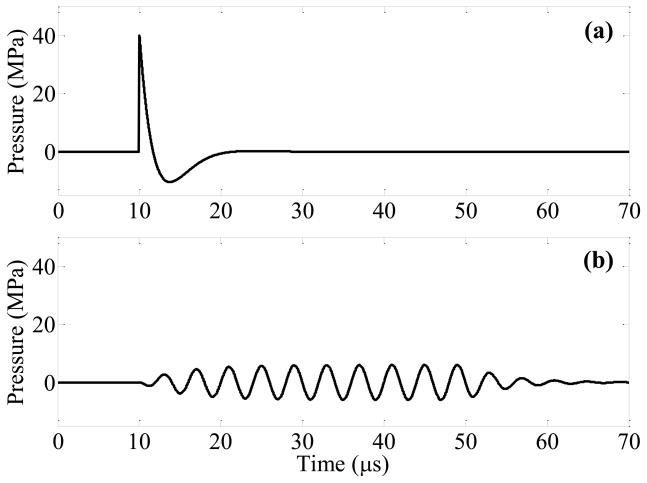
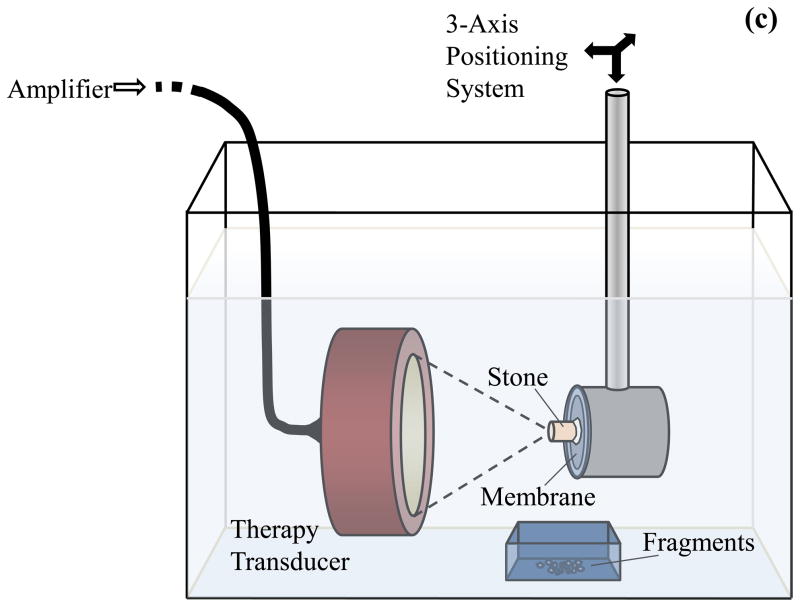
Figure 1.
Modeled focal pressure waveforms for a lithotripsy shock wave (a) and ultrasound burst wave (b). The waveform in (a) approximates the shock from a Dornier HM3 lithotripter, while the burst wave in (b) corresponds with the highest pressure amplitude (pa = 6.5 MPa) applied in this study. The experimental setup for exposure of stones to burst waves is shown in (c). A focused ultrasound transducer was placed in water tank, and the stone was aligned with the focus using a motorized 3-axis positioning system. The transducer was driven by an amplifier to expose the stone to ultrasound bursts. Fragments were collected in a small container positioned below the stone.