Figure 1.
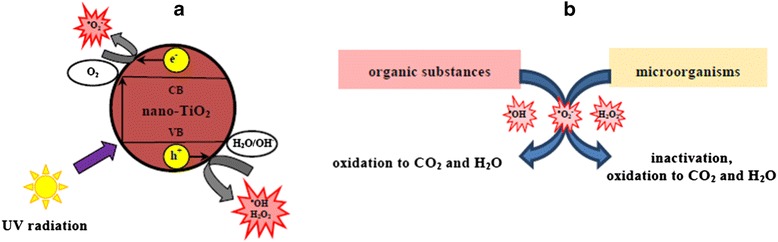
ROS generation and its effects. Mechanism of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation on the surface of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (a) and the effects of ROS activity on organic substances and microorganisms (b). On the surface of the nano-TiO2 particles, exposed to UV radiation, ROS (•O2 −, •OH, H2O2) are formed (a) that have the ability to inactivate microorganisms and to oxidize organic matter (b).
