Figure 5.
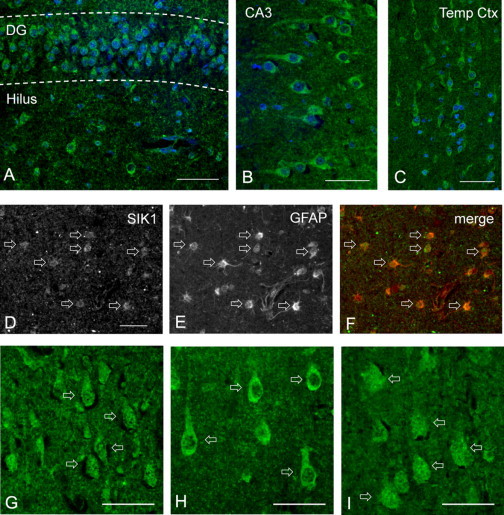
SIK1 Brain Immunohistochemistry
Formalin-fixed human brain sections from subject DB14-013 (p.Glu347∗ mutation) and two other infants were obtained from the NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders at the University of Maryland, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned at a thickness of 4 μm. Specimens were deparaffinized by incubation in xylene, followed by rehydration through graded ethanol/water solutions and equilibration in PBS. Antigen retrieval was performed by heating in 0.01 M sodium citrate (pH 6.0) in a 90°C water bath for 45 min. Specimens were then blocked in PBS with 10% donkey serum, 0.1% Triton X-100, and 2% BSA for 30 min and incubated overnight at 4°C in primary antibodies diluted in blocking solution. The SIK1 primary antibody (M01, clone 2C12, Abnova) is a mouse monoclonal IgG2a directed against an epitope mapping to the N-terminal 100 amino acids of human SIK1. Other primary antibodies included goat polyclonal MAP2 and GFAP (Santa Cruz). Slides were then incubated in fluorescent secondary antibodies at room temperature for 2 hr. After incubation in DAPI nuclear counterstain and Sudan Black to block endogenous fluorescence, sections were examined and photographed with a Nikon Eclipse Ni-U epifluorescence microscope.
(A–C) SIK1 immunofluorescence (IF) in subject DB14-013 was detected in neuronal somas and proximal dendrites within the dentate gyrus and hilus (A) and CA3 of the hippocampus (B), as well as in the temporal cortex (C).
(D–F) SIK1 expression in GFAP+ astrocytes in white matter of the temporal cortex in subject DB14-013, illustrated by staining for SIK1 (D), GFAP (E), or both (F). Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(G–I) SIK1 IF in temporal cortex of a control infant (G), subject DB14-013 (H), and an epileptic infant with normal SIK1 sequencing (I). Pyramidal neurons exhibited both nuclear and cytoplasmic SIK IF in the control and epileptic subjects, but localization predominantly in the cytoplasm in subject DB14-013. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
