Figure 5.
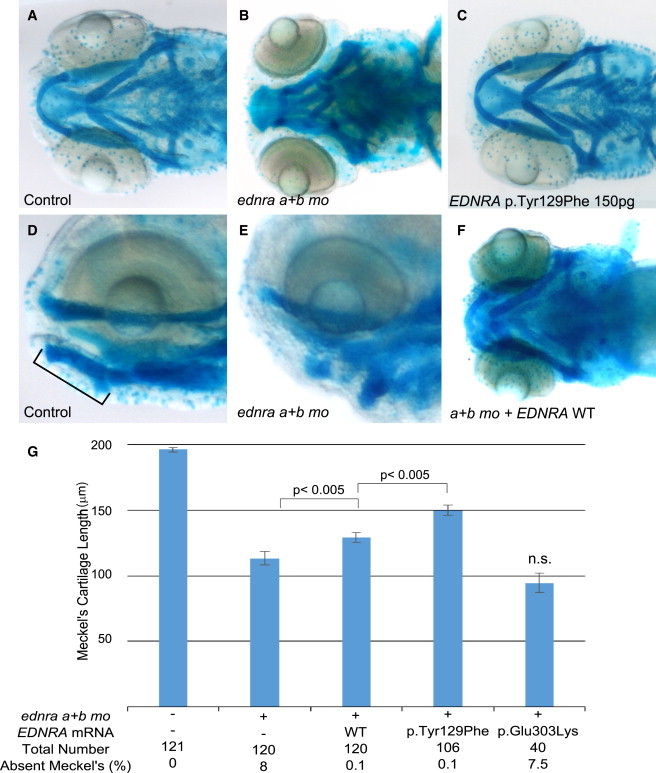
EDNRA p.Tyr129Phe but Not p.Glu303Lys Rescues Ventral Pharyngeal Arch Defects Caused by ednra Knockdown in Zebrafish
(A, B, D, and E) Ventral and lateral views of uninjected controls (A and D) and embryos injected with ednraa and ednrab morpholinos (MOs) (B and E) and stained with alcian blue. Meckel’s cartilage is indicated by a bar in (D).
(C) Injection of mRNA encoding human EDNRA p.Tyr129Phe (150 pg) did not result in a discernable phenotype.
(F) Injection of mRNA encoding wild-type (WT) human EDNRA partially rescues the ventral cartilage defect induced by MO knock-down of the zebrafish ednra orthologs.
(G) Bar graphs showing measurements of the length of Meckel’s cartilage. The first column represents uninjected embryos. For each co-injection, 100 pg of mRNA was injected. Meckel’s cartilage reduction is rescued significantly by both EDNRA WT and EDNRA p.Tyr129Phe-encoding mRNAs but not by EDNRA p.Glu303Lys-encoding mRNA. Statistical significance (Student’s t test) is denoted by p values or n.s. (not significant) on the bar graphs. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Data are from three independent experiments.
