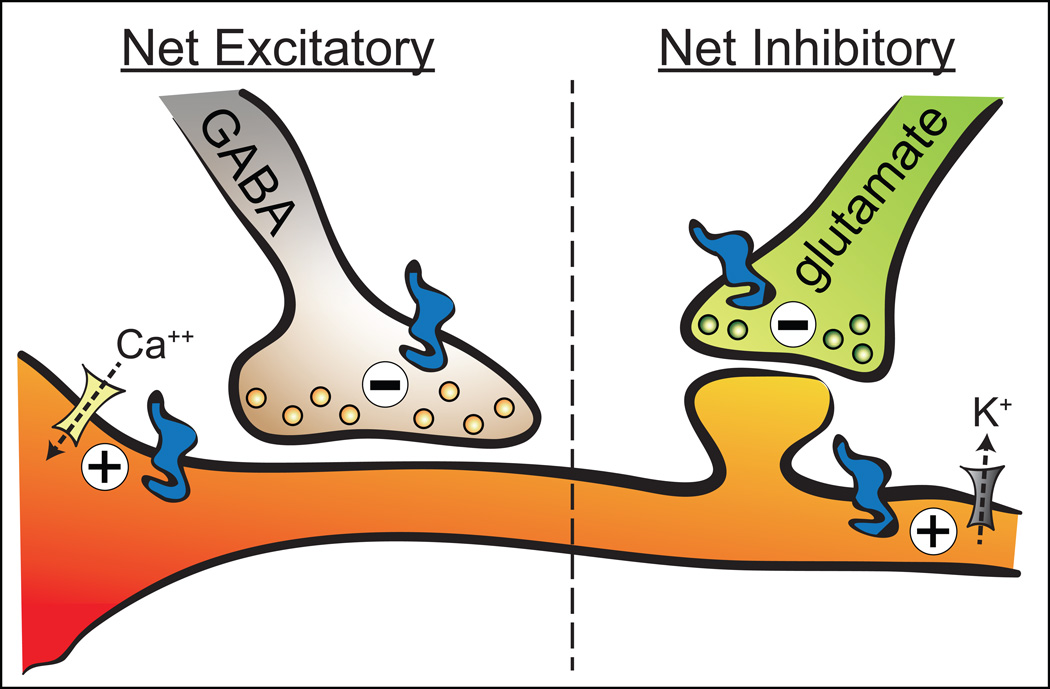
Figure 4.
Major pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms underlying MOP receptor (blue icon) control of VTA neurons. MOP receptor control of VTA neurons can have a net excitatory effect (directly by increasing Ca++ channel (yellow icon) conductance or indirectly by inhibiting GABA release) or a net inhibitory effect (directly by activating K+ channels (gray icon) or indirectly by inhibiting glutamate release).