Figure 2.
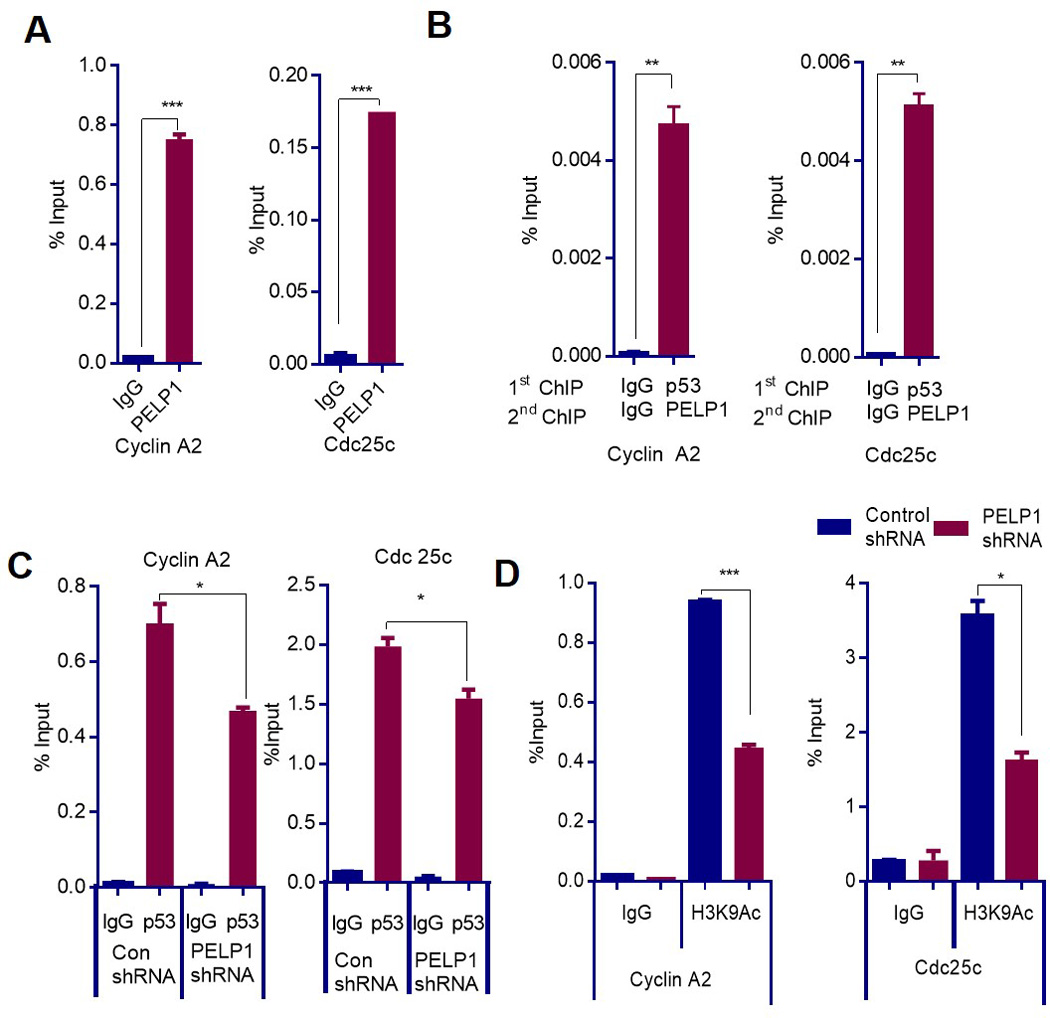
PELP1 recruits and regulates histone modifications on MTp53 target gene promoters. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with camptothecin for 6 h and were subjected to ChIP assay using the PELP1 antibody. PELP1 recruitment was analyzed by qRT-PCR with primers specific for NF-Y binding elements on the Cdc25c and Cyclin A2 promoters. *** P<0.001. (B) Sequential ChIP was performed on MDA-MB-231 cells that were treated with camptothecin for 6 h. Initial ChIP was performed using IgG or p53 antibody followed by re-ChIP using IgG or PELP1. qRT-PCR was performed in duplicates with primers specific for Cyclin A2 and Cdc25c. **P < 0.01. (C) MDA-MB-231 cells expressing control- or PELP1-shRNA were treated with camptothecin for 6 h and were subjected to ChIP assay using p53 antibody. Recruitment of MTp53 was analyzed using qRT-PCR with primers specific for NF-Y binding elements on the Cdc25c and Cyclin A2 promoters. *, P<0.05; (D) MDA-MB-231 cells expressing control- or PELP1-shRNA were treated with camptothecin for 6 h, chromatin was isolated and subjected to ChIP assay using the H3K9Ac antibody. The status of the H3K9Ac mark was analyzed using qRT-PCR with primers specific for NF-Y binding elements on the Cdc25c and Cyclin A2 promoters.*, P<0.05; *** P<0.001.
