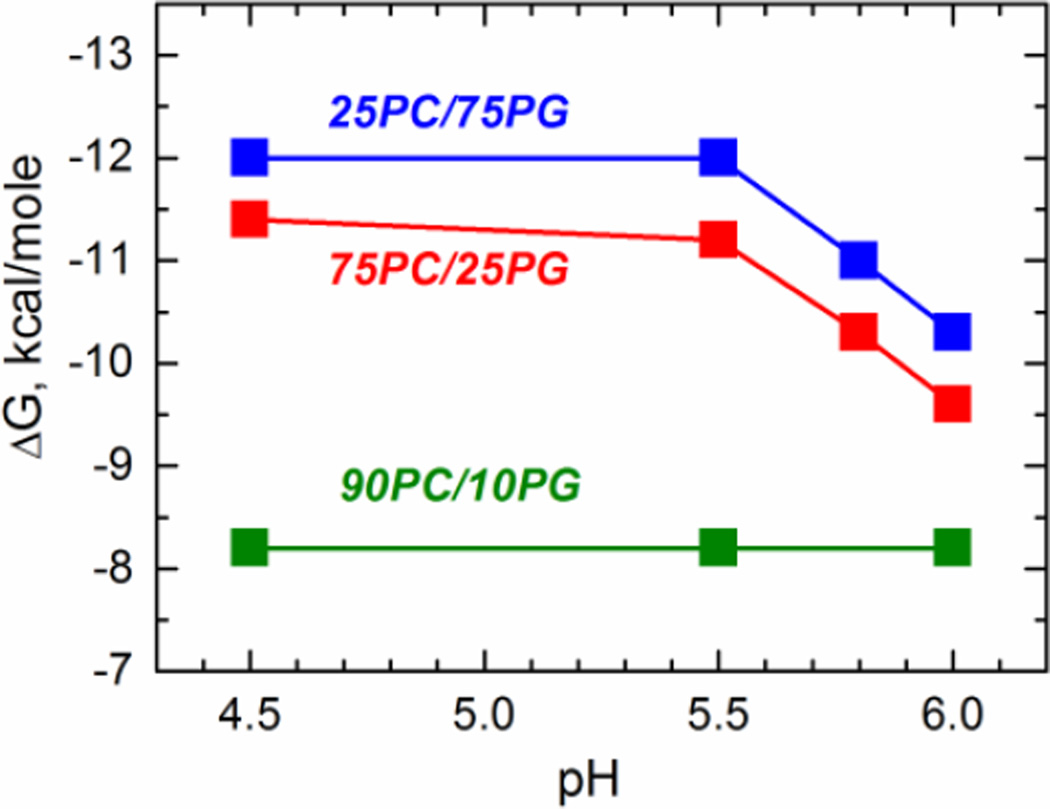
Fig. 7.
pH-dependence of the free energy of interfacial membrane binding (90PC/10PG, olive) and transmembrane insertion (75PC/25PG, red; 25PC/75PG, blue) for the diphtheria toxin T-domain WT. The free energy of binding to lipid vesicles with formation of trapped interfacial intermediate state is close to −8 kcal/mole, and is pH-independent. The free energy difference between the transmembrane T-state and the interfacial I-state ranges from −1.5 to −4 kcal/mol depending on membrane composition and the pH.