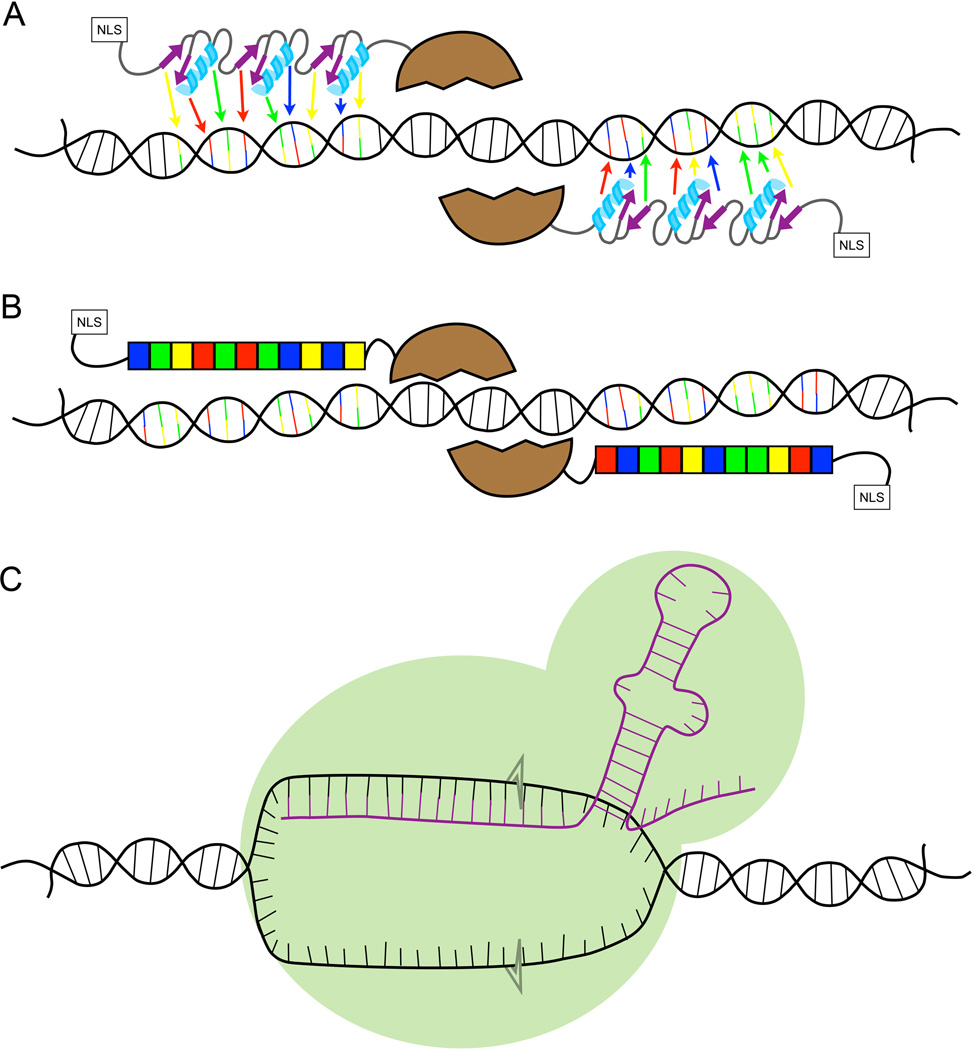
Figure 1. Diagrams of each of the double strand break technologies.
A) ZFNs are made from two different arms that each typically comprise of three binding proteins recognizing three bases each, depicted by the arrows pointing to the bases to which the individual motifs would bind. Attached to the N-terminus is the nuclease domain from the FokI restriction enzyme. This dimeric protein creates double strand breaks. On the opposite end is the nuclear localization signal (NLS) B) TALENs are made of repeats that have two amino acids in the center required for sequence-specific DNA binding. Each repeat binds a single DNA base, represented by the boxes of the same color as the base to which it binds. C) The CRISPR/Cas9 system requires an RNA (shown in purple) that hybridizes to the unwound DNA. The Cas 9 protein (the green surrounding the RNA) creates the double strand breaks at the DNA/RNA hybrid.