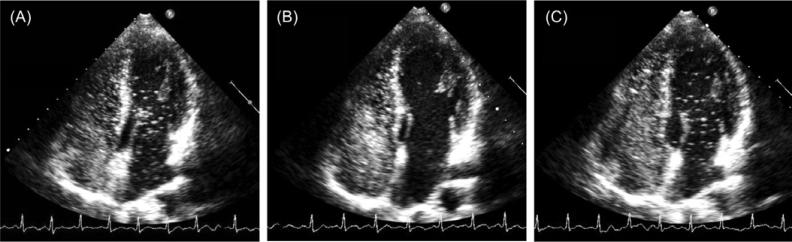
Fig. 3.
Prevention of transpulmonary passage of saline contrast bubbles with exercise in hyperoxia. Saline contrast echocardiograms from a 36-year-old male subject during exercise at 180 W in normoxia and hyperoxia. (A) echocardiogram during exercise for 1 min at 180 W in normoxia. Note saline contrast bubbles in the left heart indicating arteriovenous shunting. Bubble score = 3. (B) Echocardiogram during exercise for 120 s at 180 W in hyperoxia (100% O2). Note absence of saline contrast bubbles in the left heart indicating no arteriovenous shunting. Bubble score = 0. (C) Echocardiogram upon returning to exercise for 60 s at 180 W in normoxia. Note appearance of saline contrast bubbles in the left heart recommenced indicating arteriovenous shunting. Bubble score = 3. (From Lovering AT, Stickland MK, Amann M, Murphy JC, O'Brien MJ, Hokanson JS, Eldridge MW. Hyperoxia prevents exercise-induced intrapulmonary arteriovenous shunt in healthy humans. J Physiol. 2008 Sep 15;586(Pt 18):4559–65; with permission.)