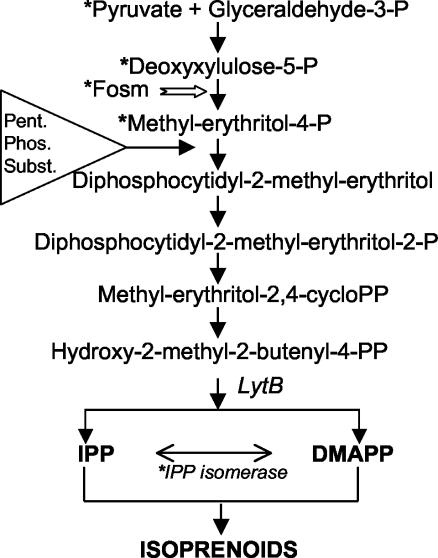
FIG. 1.
The isoprenoid biosynthetic MEP pathway as determined for E. coli beginning with PYR plus GA3P leading to the formation of MEP from DXP and through subsequent steps via the LytB enzyme to IPP and DMAPP (3, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20, 30). Fosmidomycin (white arrow) inhibits the synthesis of MEP and blocks the growth of the bacterium. Asterisks denote differences in Synechocystis strain PCC 6803 where PYR, DXP, and MEP do not serve as substrates in vitro; where IPP isomerase activity has not been observed; and where fosmidomycin does not inhibit isoprenoid biosynthesis or growth in the cyanobacterium (6), and the triangle indicates where pentose phosphate cycle substrates may possibly enter downstream of MEP.