Figure 3. NA treatment abolishes RIPK1 ubiquitination and activates the NF-κB non-canonical pathway.
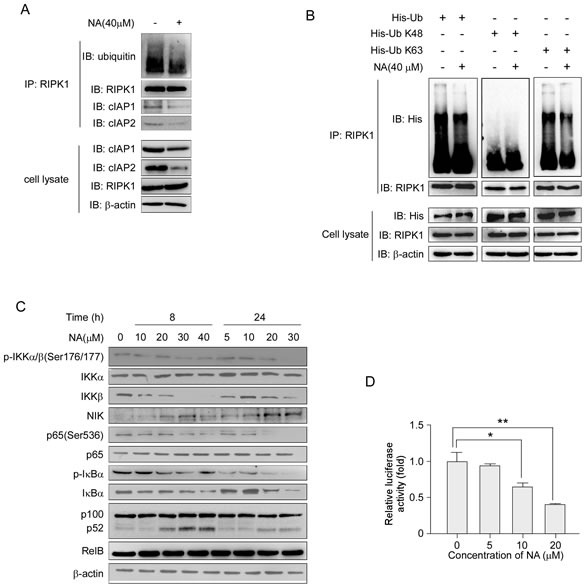
A. C666-1 cells were treated or not treated with 40 μM NA for 8 h, and RIPK1 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted. β-Actin served as a loading control. B. Cells were transfected with the His-Ub (wt, K48, K63) plasmids for 48 h, then treated or not treated with 40 μM NA for 8 h. RIPK1 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted. β-Actin served as a loading control. C. The effect of increasing doses of NA (0-40 μM) treatment for 8 or 24 h on the expression level of IKKα, IKKβ and NIK and downstream molecules, p65, p100, p52 and IκBα was analyzed by immunoblotting. β-Actin served as a loading control. D. NA inhibits NF-κB reporter gene expression. C666-1 cells were transiently transfected with an NF-κB-containing plasmid for 24 h. After transfection, cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of NA for 24 h. Gene expression was assayed by measuring luciferase activity.
