Figure 1. EPOR down regulation leads to a cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase and polyploidy.
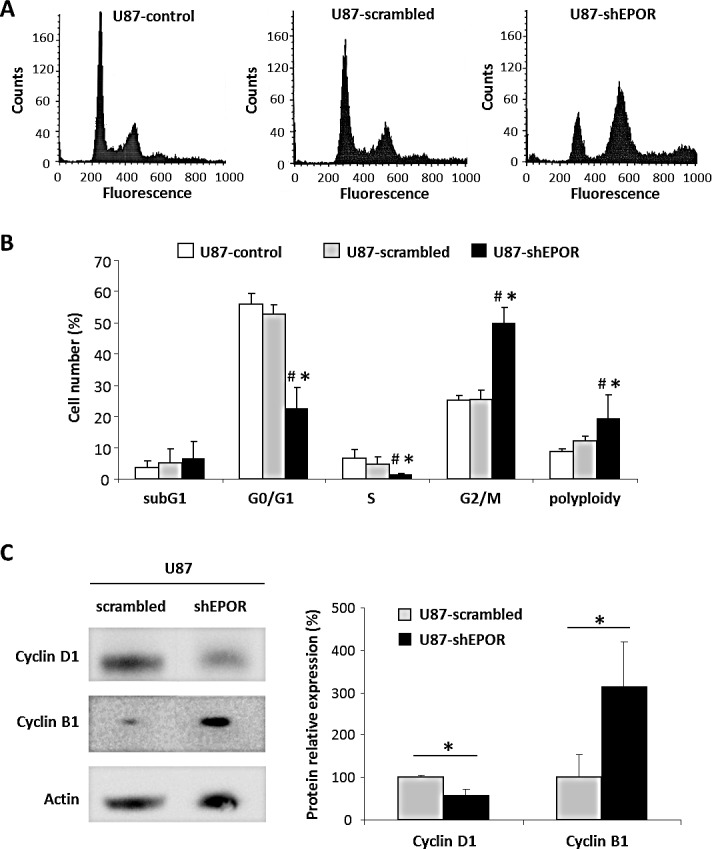
At about 80% confluence, infected or not U87 cells were fixed and stained with propidium iodide to determine cell cycle status by flow cytometry or proteins of these cells were extracted to study by western blotting the expression of proteins involved in cell cycle progression. (A) Cell cycle profiles of U87-control, U87-scrambled and U87-shEPOR. (B) Quantification of the cell distribution in different phases of cell cycle. Mean ± SD, n=4 for each cell type; # p<0.05 control cells and * p<0.05 vs scrambled shRNA infected cells (Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test after a significant ANOVA). (C) Representative western blots on U87-scrambled and U87-shEPOR cells and quantitative analyses of cyclin D1, an important regulator of G1 to S phase progression, and cyclin B1 which is involved in G2/M cell cycle arrest. Mean ± SD, n=3 for each cell type; * p<0.05 vs scrambled shRNA infected cells (Student's t-test).
