Figure 6. The tylophorine compounds downregulate c-Myc protein levels and affect the expression of c-Myc target genes in carcinoma cells treated with tylophorine compounds in vitro or in vivo.
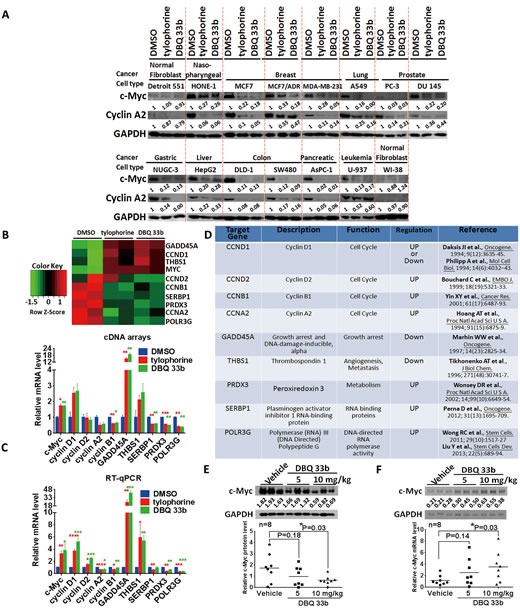
A. Tylophorine and a tylophorine-derived-dibenzoquinoline 33b (DBQ 33b) inhibited the protein expression of c-Myc in 13 carcinoma and 2 fibroblast cell lines. The results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. B-D. The effects of tylophorine on the expression of c-Myc target genes. The results were obtained from an analysis of gene expression profiling with a cDNA-array (B) and verified by RT-qPCR (C). The genes regulated by the tylophorine compounds through c-Myc are listed by function and their upregulation or downregulation by c-Myc as determined in previous studies as indicated (D). Cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), tylophorine (2 μM), or DBQ 33b (0.5 μM) for 24 h prior to lysis for western analysis with the indicated antibodies (A) or prior to mRNA extraction for gene expression profiling using the Illumina-HumanHT-12-v4 Expression-BeadChip (B) and RT-qPCR analysis (C). E & F. The protein (E) and mRNA (F) expression levels of c-Myc were downregulated in vivo in A549 xenograft tumors in mice by treatment with DBQ 33b [22]. (E) The protein expression of c-Myc detected by immunoblot analysis (upper panel) was quantitated and shown individually (lower panel). (F) The mRNA expression of c-Myc was analyzed by RT-qPCR; the products were shown in the upper panel, and the individual data were plotted in the lower panel. The relative expression levels of mRNA or protein were normalized with their respective internal loading control GAPDH. The sequences of the gene primer pairs used were listed in Supplemental Table 3. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.005; ***, p<0.0005; ****, p<0.0001.
