Figure 3. Validation of the CIP2A-PP2A-AKT pathway.
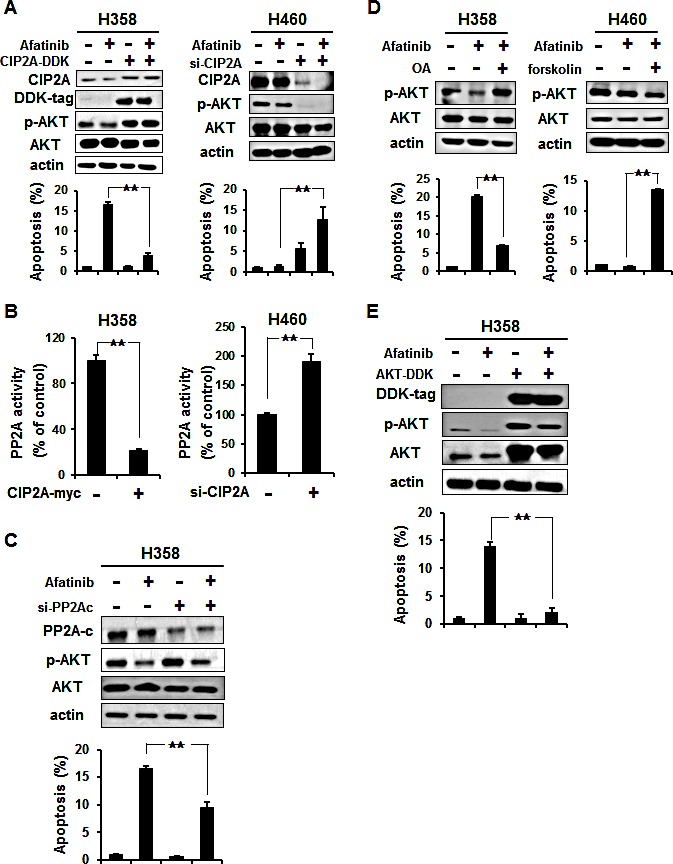
(A) Left, ectopic expression of CIP2A (CIP2A-DDK) increased p-AKT and attenuated the effects of afatinib on apoptosis of H358 cells. H358 cells overexpressing CIP2A were treated with 10 μM afatinib for 24 h. Right, knockdown of CIP2A expression by siRNA increased the sensitivity to afatinib-induced apoptosis in H460 cells. Cells were transfected with either control or CIP2A siRNA for 48 h then exposed to 10 μM afatinib for 24 h. (B) Left, overexpression of CIP2A decreased PP2A activity in H358 cells. Right, downregulation of CIP2A by siRNA increased the activity of PP2A in H460 cells. (C) Silencing PP2Ac reduced the apoptotic effect of afatinib in H358 cells. Cells were transfected with either control or PP2Ac siRNA for 48 h then exposed to 10 μM afatinib for 24 h. (D) Left, okadaic acid (OA), a PP2A inhibitor, increased p-AKT and inhibited the effects of afatinib on apoptosis of H358 cells. Right, forskolin, a PP2A agonist, sensitized resistant H460 cells to afatinib. Data are mean ± SD. n = 3 for each condition. **, p < 0.01, vs. no afatinib. (E) Ectopic expression of AKT (AKT-DDK) attenuated the effects of afatinib on apoptosis of H358 cells. H358 cells overexpressing AKT were treated with 10 μM afatinib for 24 h.
