Figure 1. Transforming potential of the D797N Vav mutant.
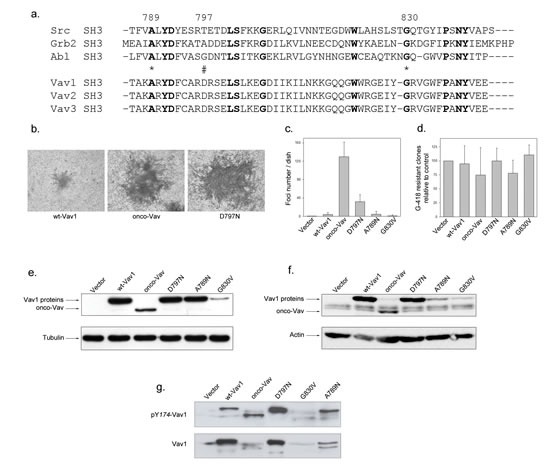
a. Sequence alignment of SH3 domains containing proteins. SH3 domains of Src, Grb2 and Abl are used as a reference for Vav1-2-3 C-terminal SH3 domains. Conserved residues are in bold. Stars and double string indicate the mutated residues used in the study. b-c-d Focus formation assays. Two weeks after transfection with the indicated constructs, NIH3T3 cells were fixed, stained with Giemsa solution, observed using light microscopy (b, Nikon camera DXMI200F, magnification 20x) and the foci numbers were quantified (c). After selection with G-418, neo-resistant clones were counted relative to transfection with empty vector (d). Results are the mean of four independent experiments ± standard deviation. e-f. Vav1 proteins expression. Cell extracts from 48h transient transfections (e) or G418-selected stable cell lines (f) expressing the myc-tagged Vav1 proteins were analysed by immmunobloting with anti-myc Ab (upper panel). Loading controls were assessed by detection of actin and tubulin (lower panel). g Phosphorylation levels of Vav1 proteins in stable cell lines. Proteins were analysed by immmunobloting using phospho Tyr174-Vav1 antibody (upper panel) and anti-Vav1 antibody (lower panel).
