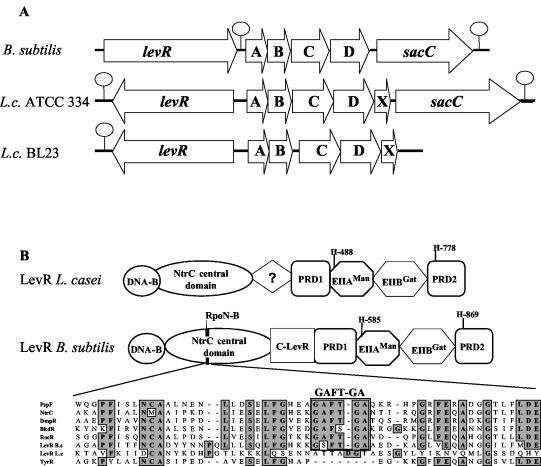
FIG. 2.
(A) Schematic representation of the lev operon and the preceding levR gene in B. subtilis and in L. casei (L.c.) strains ATCC 334 and BL23. Hairpin loops indicate transcription terminators. (B) Domain organization of the L. casei and B. subtilis transcription activator LevR. DNA-B indicates the DNA binding domain with the helix-turn-helix motif. C-LevR indicates a region located between the NtrC central domain and PRD1 in B. subtilis LevR which differs from the corresponding region in L. casei LevR. An alignment of the sequence around the RpoN binding motif GAFTGA (RpoN-B) of several proteins containing an NtrC central domain is also shown. PspF, NtrC, and TyrR are proteins from E. coli, and BkdR and RocR are from B. subtilis. The GAFTGA sequence motif is absent from TyrR and L. casei LevR, which are both RpoN independent, but is present in B. subtilis LevR, which is RpoN (SigL) dependent, and in the other transcription activators included in the alignment.