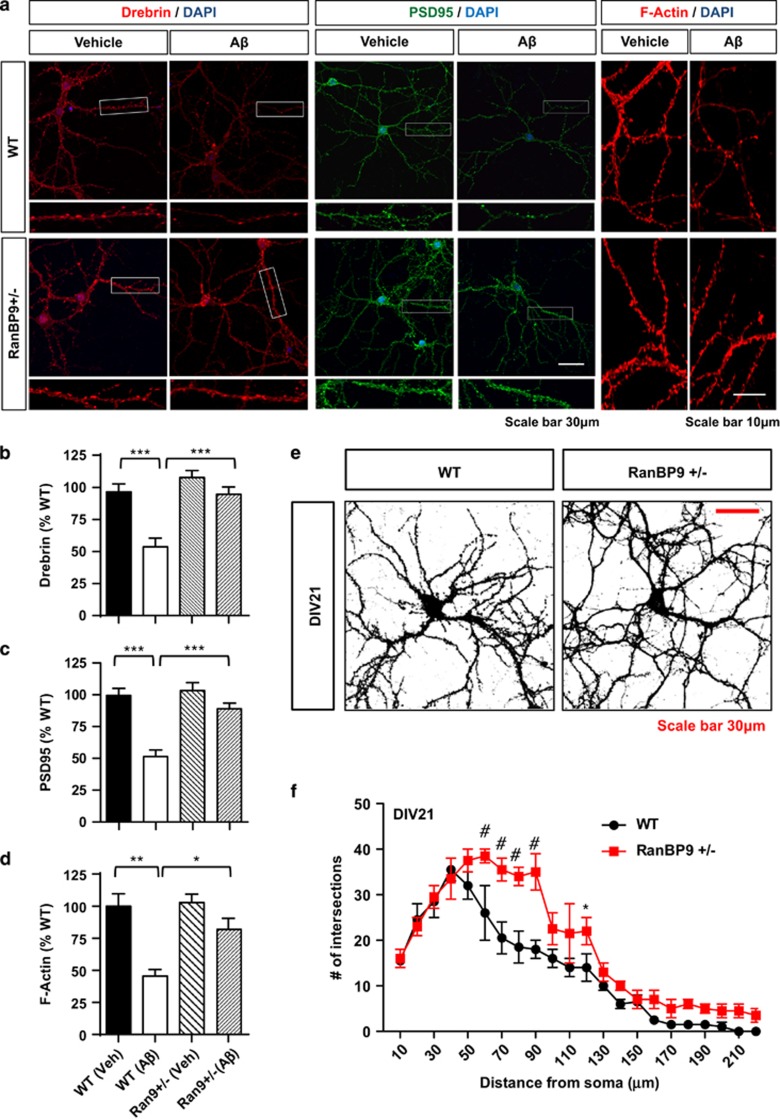
Figure 3.
RanBP9 mediates the depletion of postsynaptic proteins and F-actin induced by Aβ1-42O in mature primary hippocampal neurons. (a-d) DIV21 primary hippocampal neurons derived from P0 RanBP9+/− and WT littermate mice treated with or without Aβ1-42O (1 μM) for 2 h and subjected to immunocytochemistry for Drebrin, PSD95, and F-actin (Rhodamine-phalloidin). (a) Representative images showing Aβ1-42O-induced depletion of Drebrin, PSD95, and F-actin in WT neurons but not in RanBP9+/− neurons. (b) Quantitation of Drebrin intensity in secondary and tertiary spine-containing dendrites (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, ***P<0.0005, n=9 replicates from three pups per genotype). (c) Quantitation of PSD95 intensity in secondary and tertiary spine-containing dendrites (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, ***P<0.0005, n=10 replicates from three pups per genotype). (d) Quantitation of F-actin (Rhodamine-phalloidin) intensity in secondary and tertiary spine-containing dendrites (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, **P<0.005, *P<0.05, n=4 replicates from two pups per genotype). Error bars represent S.E.M. on graphs. (e and f) Scholl analysis of neurite arborization/elongation in WT and RanBP9+/− hippocampal neurons on DIV21. (e) Representative images of saturated F-actin stain. (f) Quantitation of neurite intersections on concentric circles from the soma in 10μm increments (10–220 μm) (two-way ANOVA, post-hoc Bonferroni, *P<0.05, #P<0.0005, n=3 replicates from two pups per genotype). Error bars represent S.E.M. in graphs