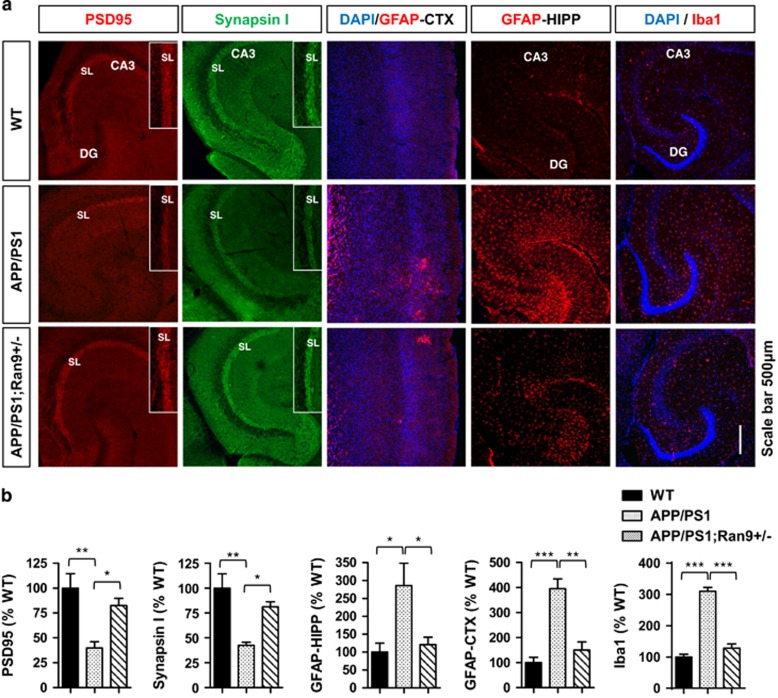
Figure 5.
RanBP9 reduction rescues neuroinflammation and synaptic protein depletion in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. (a-e) Brains from 8-month-old WT, APP/PS1, and APP/PS1;RanBP9+/− mice subjected to immunohistochemistry for GFAP (activated astrocyte marker), Iba1 (activated microglia marker), Synapsin I (presynaptic marker), and PSD95 (postsynaptic marker) in the anterior cortex (CTX) and/or hippocampus (HIPP). (a) Representative images showing RanBP9 reduction rescues neuroinflammation (GFAP and Iba1) and synaptic protein loss (Synapsin I and PSD95) in APP/PS1 mice. (b) Quantitation of PSD95 intensity within the SL of CA3 (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, *P<0.05, **P<0.005, n=4 mice per genotype, 2 F and 2 M). Quantitation of synapsin I intensity within the SL of CA3 (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, *P<0.05, **P<0.005, n=4 mice per genotype, 2 F and 2 M). Quantitation of GFAP intensity in the hippocampus (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, *P<0.05, n=4 mice per genotype, 2 F and 2 M). Quantitation of GFAP intensity in the anterior cortex (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, **P=<0.005, ***P<0.0005, n=4 mice per genotype, 2 F and 2 M). Quantification of Iba1 intensity in the hippocampus (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey, ***P<0.0005, n=4 mice per genotype, 2 F and 2 M). Error bars represent S.E.M. on graphs