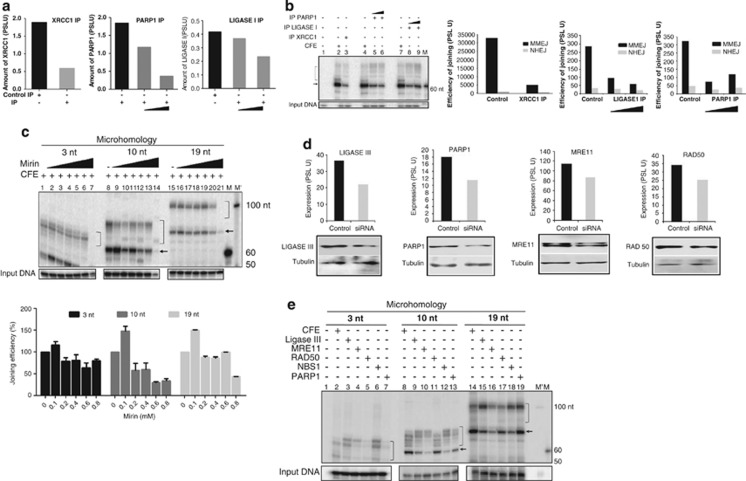
Figure 7.
Determination of proteins responsible for microhomology-mediated alternative end joining. (a) Bar diagram showing immunodepletion of XRCC1, PARP1 and LIGASE I proteins from rat testicular extracts. Lane 1, control IP. Lanes 2 and 3 are immunodepleted extract following incubation with two different concentrations of antibody (0.2 and 0.3 μg/50 μl). Following quantitation data is normalized against respective loading controls and presented. (b) Efficiency of MMEJ and C-NHEJ following immunodepletion of XRCC1 and PARP1 and LIGASE I on DNA substrates containing 10 nt microhomology. Joining assay and its quantification (%) are shown. The highest concentration (1 mM) was not considered for quantification, as it inhibited the joining in a nonspecific manner. (c) Effect of increasing concentrations of mirin, a MRN complex inhibitor, on MMEJ. Mirin (100, 200, 400, 600, 800 μM and 1 mM) was incubated with cell-free extracts of testis and 3, 10 and 19 nt microhomology-containing substrates and analyzed. Joining assay and its quantitation are presented. (d) siRNA-mediated knockdown of proteins in Reh cells. Reh was transfected with siRNA against LIGASE III, PARP1, MRE11 and RAD50, and harvested after 48 h. Cell-free extracts were prepared and efficiency of knockdown was evaluated by western blotting and quantified (shown as bar diagram). Scrambled siRNA was used as control. (e) Efficiency of MMEJ and NHEJ following siRNA-mediated knockdown of expression of LIGASE III, PARP1, MRE11, NBS1 and RAD50. MMEJ products are indicated by arrow, while NHEJ products are bracketed. M and M' are markers