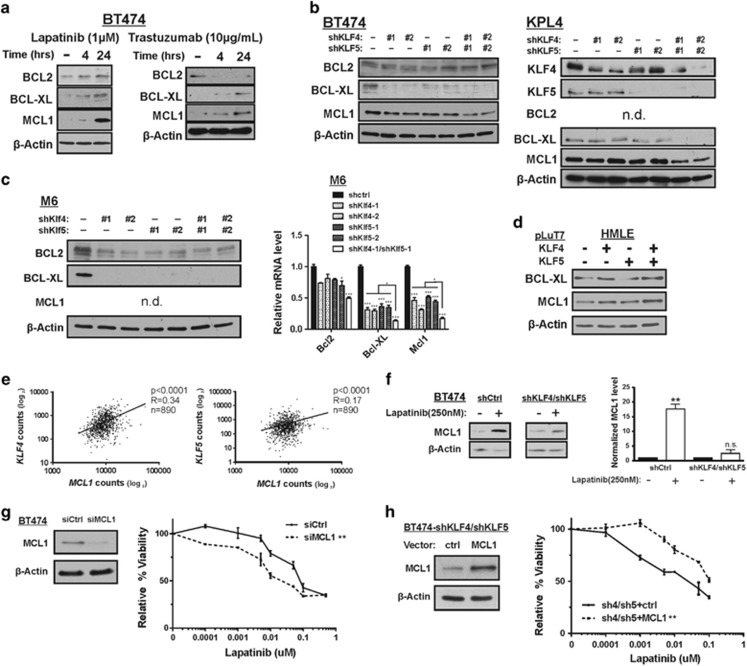
Figure 5.
KLF4/5 depletion is associated with reduced expression of anti-apoptotic BCL2 family members. (a) BT474 cells were treated with DMSO, 1 μM lapatinib, sterile water or 10 μg/ml trastuzumab for the indicated time intervals. BCL2, BCL-XL and MCL1 levels were determined by western blot analysis. (b) Protein expression was analyzed in control or KLF-depleted BT474 and KPL4 cells. (c) Protein expression (left panel) and mRNA expression (right panel) was analyzed in the indicated cell populations. (d) Protein expression was analyzed in control HMLE cells and in cells expressing ectopic KLF4 and/or KLF5. (e) Spearman's correlation between KLF4, KLF5 and MCL1 levels as determined by RNAseq analysis of 890 human breast tumors. (f) The impact of KLF4/5 knockdown on the lapatinib-mediated induction of MCL1 was determined in BT474 cells. Cells were treated with 250 nM lapatinib or DMSO for 24 h. For three independent experiments, the expression levels were quantitated using ImageJ and normalized to β-actin (bars, S.D.). (g) MCL1 levels were reduced by siRNA and the resulting cell populations were treated with lapatinib for 96 h. For each cell population, cell viability relative to the DMSO control was obtained via ATP-based luminescent assay (paired t-test, two tailed; bars, S.D.). (h) Similarly, lapatinib resistance was analyzed in KLF4/5 knockdown BT474 cells following rescue with exogenous MCL1 expression vector or empty vector control. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001