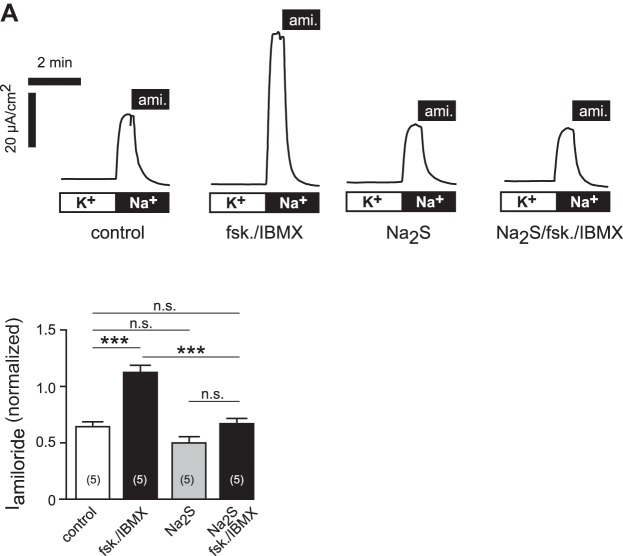
Fig. 9.
H2S prevents increase in apical membrane ENaC activity by forskolin/IBMX. A: representative current traces of Ussing chamber experiments on basolaterally permeabilized H441 monolayers. The basolateral solution contained nystatin (1.5 × 10−4 M), ouabain (2 × 10−3 M), and high K+. After permeabilization, monolayers were incubated with forskolin/IBMX (fsk./IBMX), Na2S (5 × 10−5 M), a combination thereof (Na2S/fsk./IBMX), or no drugs at all (control), and the apical membrane was subsequently changed to a high Na+ solution (gray bar) to establish an apical to basolateral sodium gradient. Amiloride (ami.; 10−5 M) was applied afterward to determine amiloride-sensitive fractions (Iamiloride) of the apical membrane. B: statistical analysis of data shown in A. Depicted are apical membrane Iamiloride, which were normalized to the initial ISC of intact monolayers before permeabilization (to compensate for alterations in baseline sodium transport capacity). Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test. ***P < 0.001. n = number within parentheses.