Figure 2.
Talin Head, but Not IBS2, Is Essential for Integrin Function at Muscle Attachment Sites
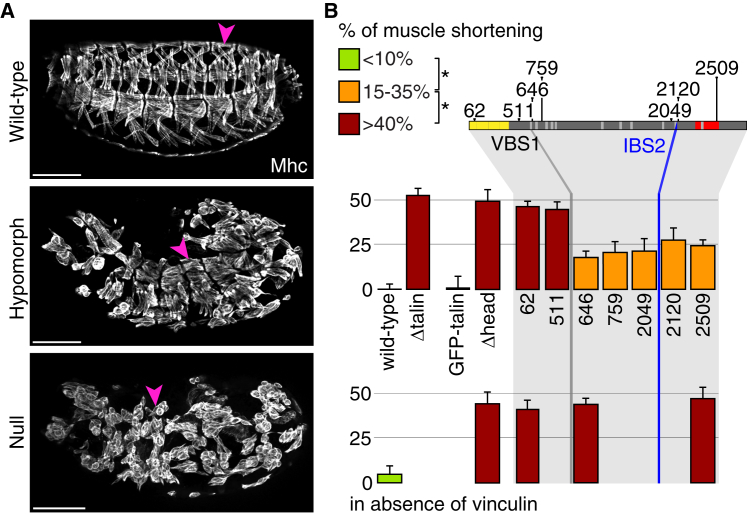
(A) Weak versus strong muscle attachment defects in talin mutant embryos. Muscle myosin heavy chain (Mhc) staining of embryonic muscles exhibiting no defect (wild-type; top), mild detachments (hypomorphic phenotype; center), or complete detachment (null phenotype; bottom). The scale bars represent 100 μm.
(B) The average shortening of five dorsal muscles (pink arrowheads in A) was quantified per embryo homozygous for the indicated mutants and plotted as the reduction in muscle length relative to wild-type in the presence (top histogram) or absence (bottom histogram) of vinculin. Bar colors show three statistically distinct categories (∗p < 0.01; green bars are not significantly different from wild-type). At least five embryos were measured per genotype. Error bars are SD. Genotypes not analyzed do not have a bar.