Figure 2.
Purification of Unanchored K29/K33 PolyUb Chains
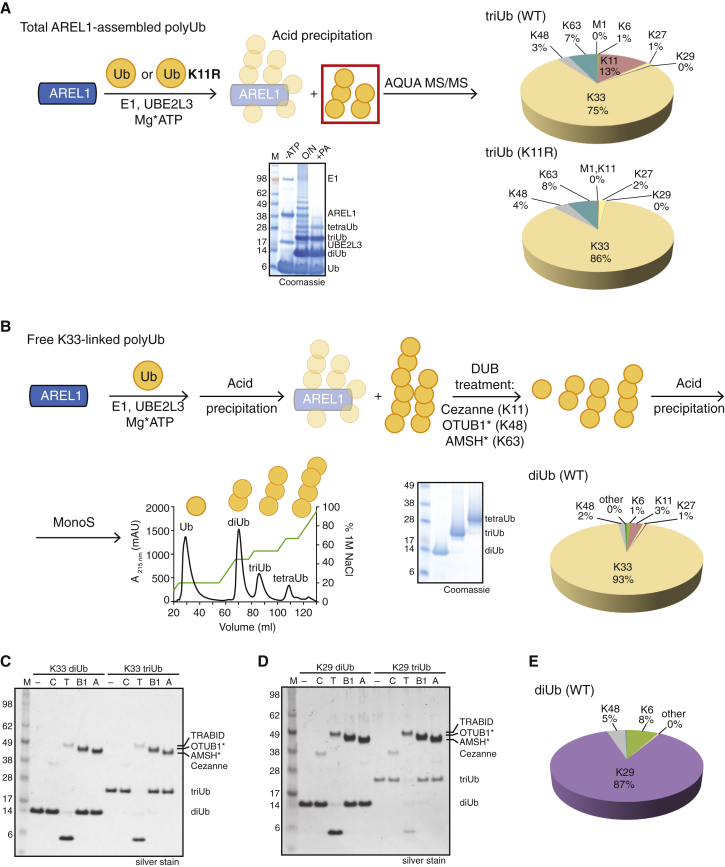
(A) Schematic of the assembly of K33-linked Ub chains using either WT or K11R Ub (top). AQUA profiles of triUb using either WT (top right) or K11R Ub (bottom right; K6 linkage was excluded from the quantitative analysis because of the K11R substitution). Bottom: corresponding SDS-PAGE gel for assembly of free chains. −ATP, initial reaction without ATP addition; O/N, overnight incubation of the assembly reaction; +PA, perchloric acid treatment of the assembly reaction.
(B) Schematic representation of the purification of K33-linked polyUb chains. Following the assembly reaction, perchloric acid treatment removes the ubiquitinated and unmodified forms of E1, E2, and E3. Linkage-selective DUBs are then used to remove undesired Ub linkages. An additional perchloric acid step is required to inactivate the DUBs prior to cation exchange chromatography (bottom), which resolves the homotypic chains based on linkage length. Bottom center: SDS-PAGE of purified K33-linked di-, tri-, and tetraUb. Bottom right: AQUA MS/MS of purified K33-linked diUb.
(C) Deubiquitinase assay of purified K33-linked di- and triUb. –, no DUB; C, 200 nM Cezanne (K11-specific); T, 350 nM TRABID (K29/K33-specific); B1, 1 μM OTUB1∗ (K48-specific); A, 1 μM AMSH∗ (K63-specific).
(D) K29-linked polyUb chains can be purified analogous to the schematic shown in (B). Purified K29-linked di- and triUb were treated with DUBs as in (C).
(E) AQUA mass spectrometry profile of purified K29 diUb.