Figure 7.
Localization of Catalytically Inactive TRABID Mutants in Cells
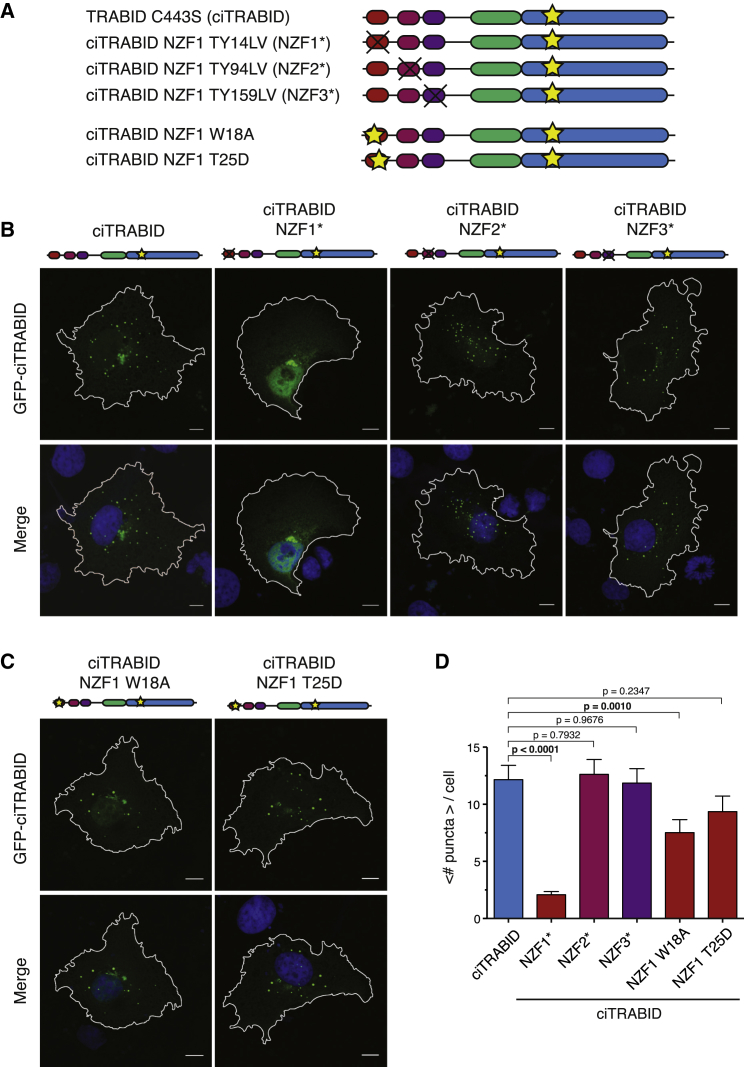
(A) Constructs used in localization experiments for GFP-TRABID fusions. Yellow stars indicate single amino acid substitutions, whereas black crosses denote two amino acid substitutions that abrogate Ub binding in the respective domain.
(B) Localization of catalytically inactive full-length GFP-TRABID (ciTRABID) constructs. GFP-ciTRABID localizes to distinct puncta in COS-7 cells. Mutations in this background that abrogate Ub binding of NZF1 (NZF1∗) lead to a significant decrease in the number of dots, whereas the equivalent mutations in NZF2 (NZF2∗) or NZF3 (NZF3∗) do not lead to a change in the number of puncta. Cartoon representations of the constructs are shown as in (A). Scale bars, 10 μm.
(C) The same experiment with single amino acid substitutions in the proximal Ub binding site of NZF1.
(D) Statistical analysis of experiments in (B) and (C) with an average number of puncta per cell for the different mutants and corresponding SEs. p Values are given in reference to the ciTRABID mutant, and significant values (α < 0.05) are shown in boldface. Error bars represent SEs.