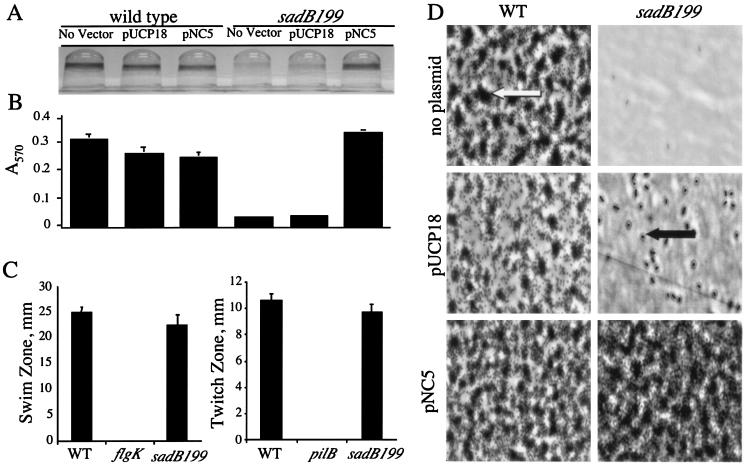
FIG. 1.
Biofilm formation phenotypes under static conditions. (A) Image of CV-stained biofilms formed by the wild type and the sadB199 mutant carrying either no plasmid, a vector control (pUCP18), or plasmid pUCP18 with the PA5346 (sadB+) ORF (pNC5). Cells were grown in minimal medium containing glucose and CAA for 24 h before being stained with CV. (B) Quantification of CV-stained wells. Ethanol was used to solubilize the CV associated with the biofilm, and the A570 of the resulting solution was measured. (C) Swimming and twitching zones were determined for the wild type and the sadB199 mutant. No swimming was observed in a control strain lacking flagella (flgK), and no twitching was observed in a control strain lacking type IV pili (pilB). (D) Direct visualization of biofilm formation on polyvinyl chloride at the air-liquid interface by phase-contrast microscopy (magnification, approximately ×1,400; see Materials and Methods for details). The large dark regions (indicated by the white arrow) represent microcolonies, the small dark rods (indicated by the black arrow) represent individual cells, and the light gray areas are the polyvinyl chloride surface. Cells were grown in minimal medium containing glucose and CAA for 24 h before washing and visualization. WT, wild type.