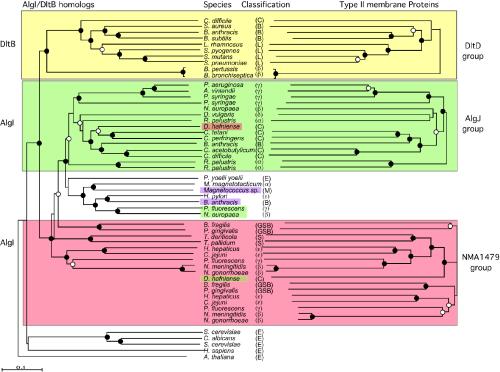
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of AlgI and DltB homologs (shown on the left-hand side) and of the type II membrane proteins encoded by genes adjacent to algI or dltB (right-hand side). Trees were constructed by using neighbor-joining and bootstrapping analysis of aligned sequences. Filled circles indicate branch points with bootstrap support of >90%. Open circles indicate branch points with bootstrap values of >70%. Branch points without circles had bootstrap values of 50 to 75%. The yellow shaded region shows the phylogeny of the DltB proteins and their genetically linked DltD protein. The green-shaded region shows the phylogeny of a subset of AlgI proteins (left) and their linked AlgJ homologs (right). The red-shaded region shows a subset of AlgI homologs and their linked homologs to NMA1479 of N. meningitidis. The pink-shaded region shows one of the Bacillus anthracis AlgI and the Magnetococcus sp. AlgI homologs that are linked to genes for type II membrane proteins related to each other but not related to the type II membrane proteins of the other three groups. Desulfitobacterium hafniense encodes an AlgI homolog closely related to the P. aeruginosa AlgI clade but a type II membrane protein related to N. meningitidis NMA1479. Also shown are AlgI/DltB homolog eukaryotes. Classifications: C, Clostridiales; B, Bacillales; L, Lactobacillales; β, β-proteobacteria; γ, γ-proteobacteria; δ, δ-proteobacteria; α, α-proteobacteria; M, Magnetococcus sp.; GSB, green sulfur bacteria; S, Spirochaetales; E, eukaryotes.