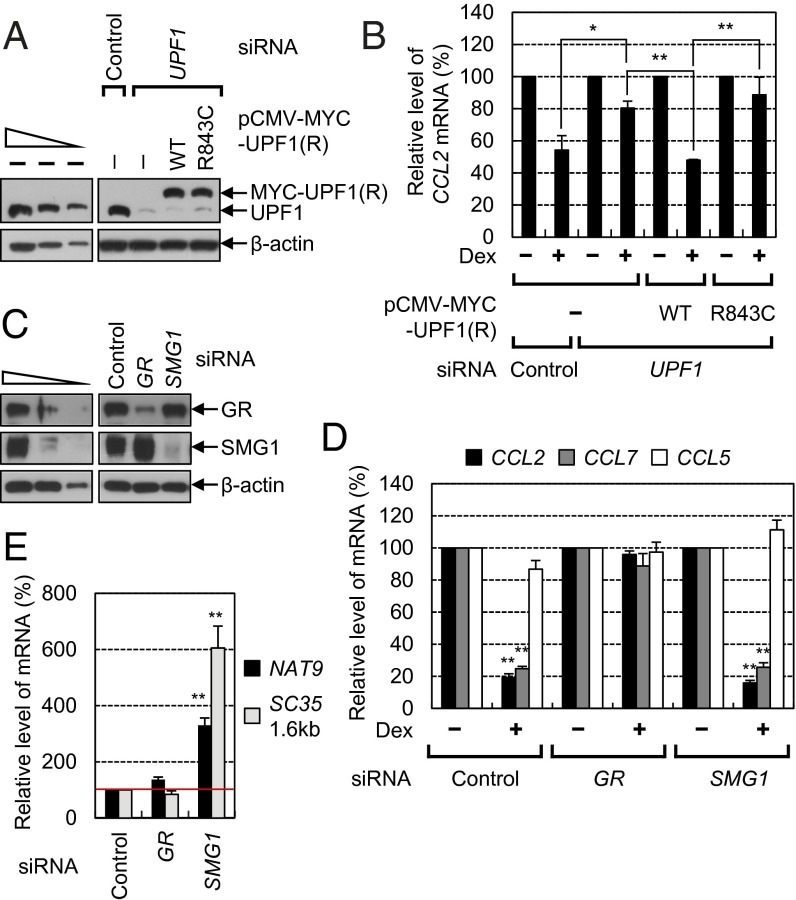
Fig. 7.
GMD requires a helicase activity but not phosphorylation of UPF1. (A and B) Complementation experiments using siRNA-resistant UPF1-WT and its R843C variant. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with either UPF1 siRNA or a nonspecific control siRNA. One day after the transfection, the cells were retransfected with a plasmid expressing siRNA-resistant MYC-UPF1(R)-WT or -R843C. Two days later, the cells were either treated or not treated with Dex for 1 h before harvesting. (A) Western blots demonstrating selective down-regulation of UPF1 and comparable levels of exogenously expressed UPF1(R) and endogenous UPF1. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of endogenous CCL2 mRNA. The levels of endogenous CCL2 mRNA were normalized to the levels of endogenous GAPDH mRNAs. The normalized levels of endogenous CCL2 mRNA in the cells not treated with Dex were arbitrarily set to 100%. (C–E) GMD is not dependent on SMG1 activity. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with GR siRNA, SMG1 siRNA, or a nonspecific control siRNA. Three days later, the cells were either treated or not treated with Dex for 3 h before harvesting. (C) Western blots demonstrating selective down-regulation of GR and SMG1 by siRNAs. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of endogenous CCL2, CCL7, and CCL5 mRNAs. The levels of endogenous GMD substrates were normalized to the levels of endogenous GAPDH mRNAs. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of endogenous NAT9 and SC35 (1.6 kb) mRNAs. The columns and bars represent the mean and SD of three independent biological replicates. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05.