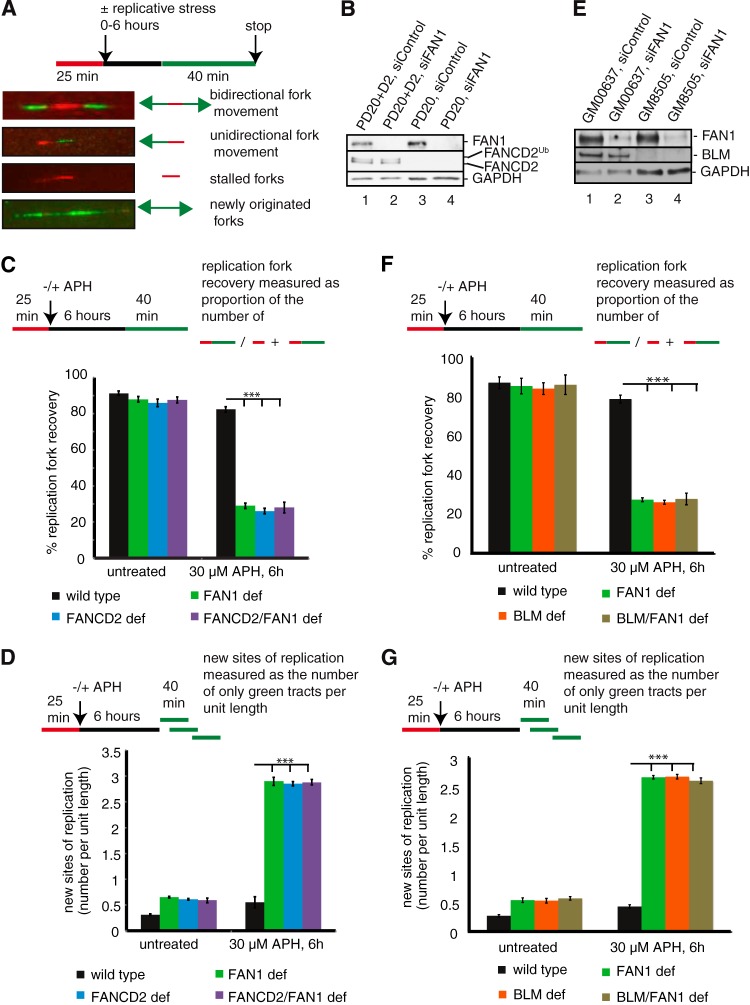
FIG 2.
FAN1 acts in the same pathway with FANCD2 and BLM to mediate restart of APH-stalled replication forks and suppression of new origin firing. (A) Schematic of DNA fibers depicting sites of replication. Red tracts, DigU; green tracts, BioU. (B) Cell types used for DNA fiber analysis in panels C and D. Cells included wild-type (PD20+D2, siControl), FAN1-deficient (PD20+D2, siFAN1), FANCD2-deficient (PD20, siControl), and FANCD2-FAN1-double-deficient (PD20, siFAN1) cells. (C) FAN1 and FANCD2 act in a common pathway to mediate replication fork restart after APH-induced fork blockade. The efficiencies of replication restart in wild-type, FAN1-deficient, FANCD2-deficient, and FANCD2-FAN1-double-deficient cells were measured as the number of restarted replication forks (DigU-BioU tracts) compared with the total number of DigU-labeled tracts (DigU plus DigU-BioU). (D) FAN1 and FANCD2 act in concert to suppress new origin firing during replication blockade. The numbers of new sites of replication originating during the 40-min recovery period after APH treatment were compared between wild-type, FAN1-deficient, FANCD2-deficient, and FANCD2-FAN1-double-deficient cells. New origins of replication were measured as the number of green-only (BioU) tracts per unit length. (E) Cell types used for DNA fiber analysis in panels F and G. Cells included wild-type (GM00637, siControl), FAN1-deficient (GM00637, siFAN1), BLM-deficient (GM08505, siControl), and BLM-FAN1-double-deficient (GM08505, siFAN1) cells. (F) FAN1 and BLM act in a common pathway to mediate replication fork restart after APH-induced fork blockade. The efficiencies of replication restart in wild-type, BLM-deficient, FAN1-deficient, and BLM-FAN1-double-deficient cells were measured as described for panel C. (G) FAN1 and BLM act in concert to suppress new origin firing during replication blockade. The numbers of new sites of replication originating during the 40-min recovery period after APH treatment were compared between wild-type, BLM-deficient, FAN1-deficient, and BLM-FAN1-double-deficient cells. New origins of replication were measured as the number of green-only (BioU) tracts per unit length.