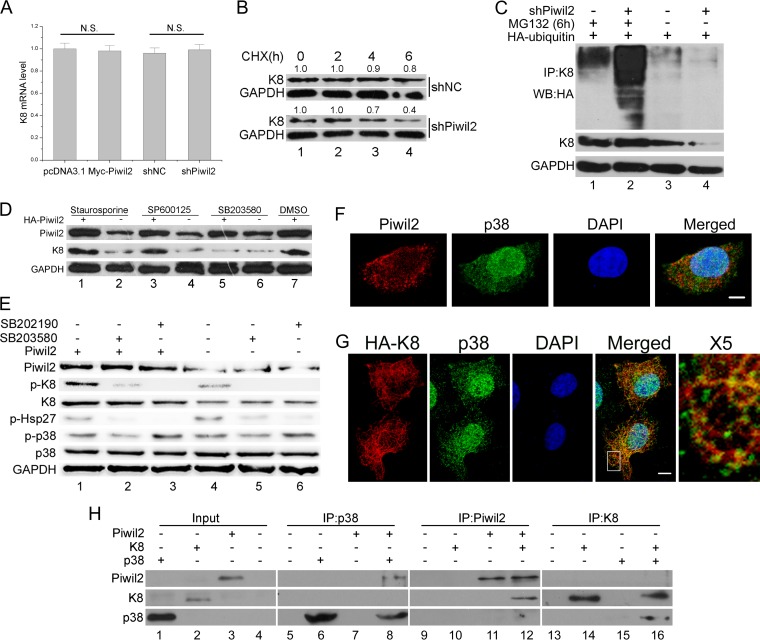
FIG 4.
Piwil2 inhibits degradation of K8 in a phosphorylation-modulated fashion. (A) Real-time PCR confirmed that the K8 mRNA level remains unchanged after Piwil2 overexpression or Piwil2 knockdown. N.S., P > 0.05 by the Student's t test. (B) Stability analysis of K8 protein. The cells transfected with shNC or shPiwil2 were treated with cycloheximide (CHX) at 5 mg/ml for 0 to 6 h. (C) Piwil2 knockdown improved K8 ubiquitination. HeLa cells were cotransfected with shPiwil2 and HA-ubiquitin plasmids. After 48 h, they were treated with MG132 for 6 h as indicated. K8 was precipitated with anti-K8 antibody, and the ubiquitination and degradation of K8 were determined by anti-HA-ubiquitin and anti-K8 immunoblotting. (D) P38 inhibitor blocks Piwil2 from upregulating K8. Cells were transfected with Myc-Piwil2 or pcDNA3.1 and treated with p38, PKC, and JNK inhibitors for 6 h. DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide. (E) P38 is involved in Piwil2-induced K8 phosphorylation. The inhibition of p38 using SB203580 or SB202190 (1 h of treatment) reduces the Ser-73 phosphorylation of K8, as shown by Western blotting. The level of p-HSP27 showed that inhibitors are working. (F) Colocalization between endogenous Piwil2 and p38. Cells were stained by anti-Piwil2 and anti-p38. (G) Colocalization between K8 and p38. Cells were transfected with HA-K8 vector and harvested for immunofluorescence assay with anti-HA and anti-p38 antibodies. Scale bars, 5 μm. The indicated region in the merged panel was shown at a higher resolution (500%) in the X5 panel. (H) Piwil2, p38, and K8 directly interact in vitro. Cell-free Piwil2, p38, and K8 protein expression was carried out using a TnT system separately, mixed together in binding buffer with protease inhibitors, and incubated on a rotating platform at 4°C for 3 h. Error bars indicate SE (N.S., P > 0.05).