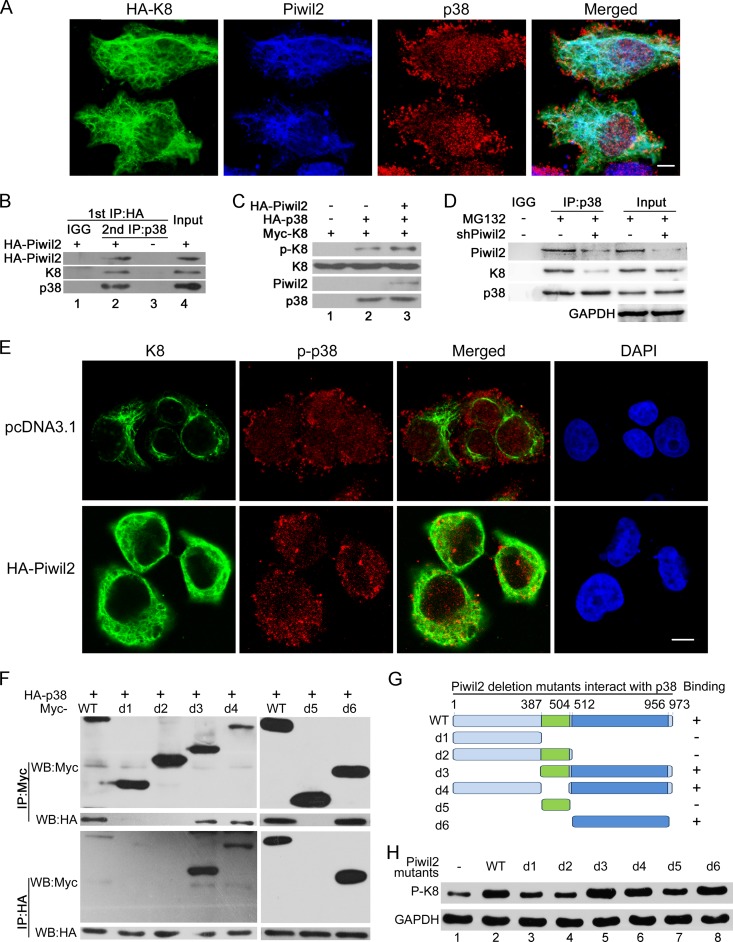
FIG 5.
Piwil2 facilitates the interaction of K8 and p38. (A) Colocalization of K8, Piwil2, and p38. Cells were transfected with HA-K8 vector and harvested for immunofluorescence assay with goat anti-HA, rabbit anti-Piwil2, and mouse anti-p38 antibodies. (B) Co-IP assay of the Piwil2-p38-K8 complex. Cells were transfected with HA-Piwil2, the lysates were subjected to anti-HA antibody immunoprecipitation and eluted by HA peptide, and then they were reimmunoprecipitated by anti-p38 antibody followed by Western blotting. (C) In vitro phosphorylation of K8. HA-Piwil2 and HA-p38 were translated and purified in vitro. Myc-K8 was translated in vitro and immunoprecipitated by Myc antibody with beads. The beads with Myc-K8 were subjected to in vitro phosphorylation in kinase buffer for 1 h with p38 or Piwil2 as indicated, followed by Western bolt analysis. (D) After 48 h, cells were transfected with shPiwil2 or shNC vector and treated with MG132 for 6 h. The lysates were subjected to anti-p38 immunoprecipitation followed by WB. (E) Piwil2 enhanced the colocalization of p-p38 and K8 in cytoplasm. HeLa cells were transfected with pc-DNA3.1 or HA-Piwil2 vector and harvested for immunofluorescence assay with anti-K8 and anti-p-p38 antibodies. Scale bars, 5 μm. (F) Interaction between different HA-p38 and different Piwil2 mutants with Myc tag. (G) Schematic of different Piwil2 mutants binding to p38. (H) The effect of different Piwil2 mutants on phosphorylation of K8 by Western blotting.