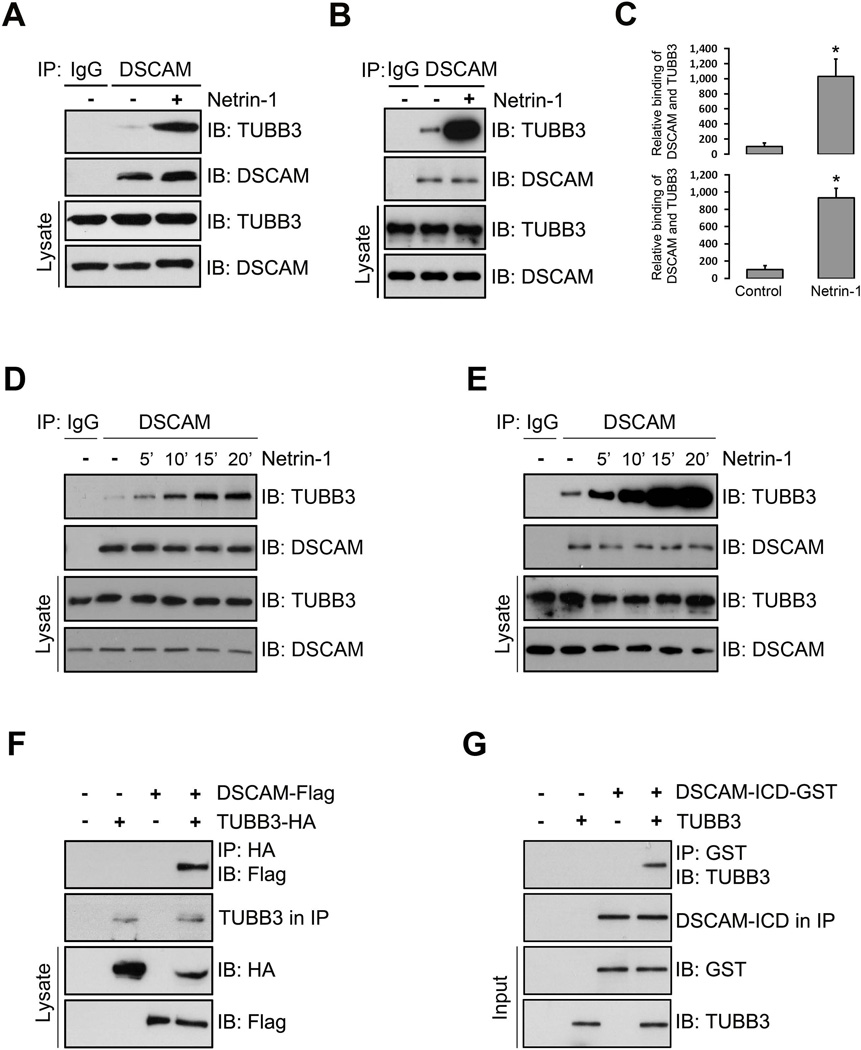
Figure 1.
Interaction of DSCAM with TUBB3. (A–B) Interaction of endogenous DSCAM with TUBB3 in primary neurons. Dissociated E15 mouse cortical neurons (A) and E13 dorsal spinal cord neurons (B) were stimulated with Netrin-1 for 20 min. The anti-DSCAM antibody was used to immunoprecipitate DSCAM proteins and the blot was analyzed with the anti-TUBB3 antibody. (C) Quantification of A (upper panel) and B (lower panel) from three independent experiments. The y-axis shows relative binding of DSCAM with TUBB3 in arbitrary units. * indicates p< 0.05 (Student’s t test). (D–E) Netrin-1 increased the interaction of endogenous DSCAM with TUBB3 in a time-dependent manner. Primary E15 cortical (D) and E13 dorsal spinal cord neurons (E) were treated with Netrin-1 from 5 to 20 minutes. Lysates of dissociated neurons were immunoprecipitated with anti-DSCAM and analyzed with anti-TUBB3. (F) DSCAM interacts with TUBB3 in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with human full-length TUBB3 tagged with HA only, human full-length DSCAM-Flag only or DSCAM-Flag and TUBB3-HA together. The anti-HA antibody was used to immunoprecipitate TUBB3 and the blot was analyzed with anti-Flag or anti-HA. (G) DSCAM directly interacts with TUBB3. Purified intracellular domain of human DSCAM tagged with GST (DSCAM-GST) was incubated with purified human full length TUBB3 in vitro. The anti-GST antibody was used to immunoprecipitate DSCAM-GST and the blot was analyzed with the anti-TUBB3.