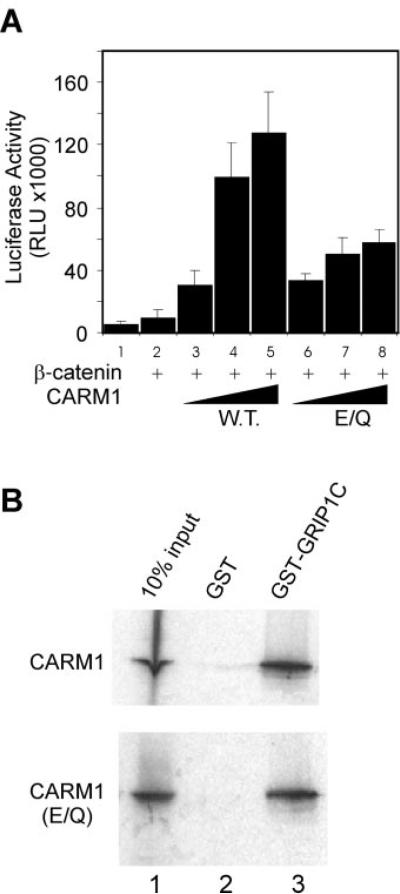
FIG. 2. Role of the methyltransferase activity of CARM1 in coactivator synergy with β-catenin.
A, CV-1 cells were transfected in 96-well plates with 20 ng of MMTV-LUC, 1 ng of AR expression vector, and the following coactivator expression vectors as indicated: β-catenin, 25 ng; CARM1 wild type (WT) or E267Q mutant (E/Q), 20, 50, or 100 ng. Transfected cultures were grown with DHT, and lucifer-ase activity was determined. Results are representative of two independent experiments. B, CARM1 wild type or E267Q (E/Q) mutant protein was translated in vitro in the presence of [35S]methionine and tested for binding to beads containing a C-terminal fragment of GRIP1 (amino acids 1122–1462) fused to glutathione S-transferase (GST-GRIP1C) or to glutathione S-transferase (GST) alone. Bound proteins were eluted (lanes 2–3) and analyzed by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. In the lane 1, 10% of the input protein was loaded on the gel.