Figure 7.
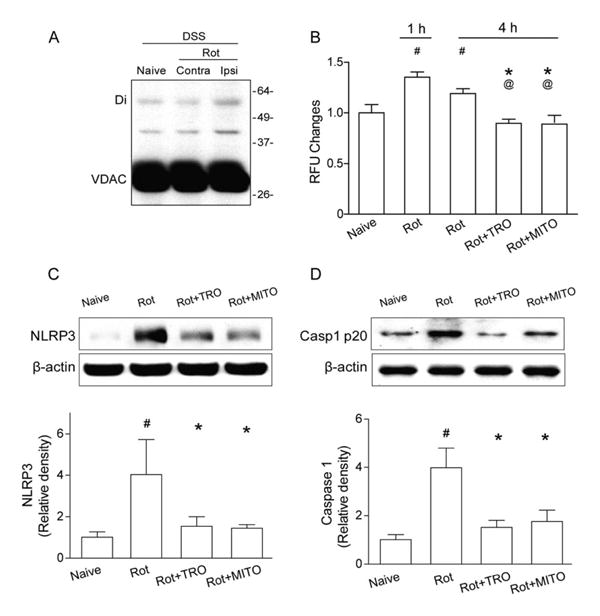
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS) promotes mitochondrial permeability transition pore formation and NLRP3 inflammasome component expression in naive animals. (A) Western blots for voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) in naive and intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) animals with chemical cross-linker (disuccinimidyl suberate [DSS]) at 1 hour following rotenone injection (Rot). Monomeric VDAC is located at 33kDa. Dimeric (Di) VDAC is detected at 45kDa. Contra=contra-lateral hemisphere; Ipsi = ipsilateral hemisphere. (B) Quantification of mROS alterations in the ipsilateral hemisphere in naive mice, 1 or 4 hours following rotenone injection (Rot), or TRO-19622 (Rot+TRO) or Mito-TEMPO treatment (Rot+MITO) 4 hours following rotenone injection; n=6 mice per group. Error bars represent mean±standard error of the mean. #p<0.05 vs naive, *p<0.05 vs Rot 1 hour; @p<0.05 vs Rot 4 hours. (C, D) Western blot assay for the expression of NLRP3 (C) and caspase-1 p20 subunit (D) in the ipsilateral hemisphere in naive, Rot, ICH+TRO, and ICH+MITO groups at 4 hours following operation; n=6 mice per group. #p<0.05 vs naive, *p<0.05 vs Rot.
