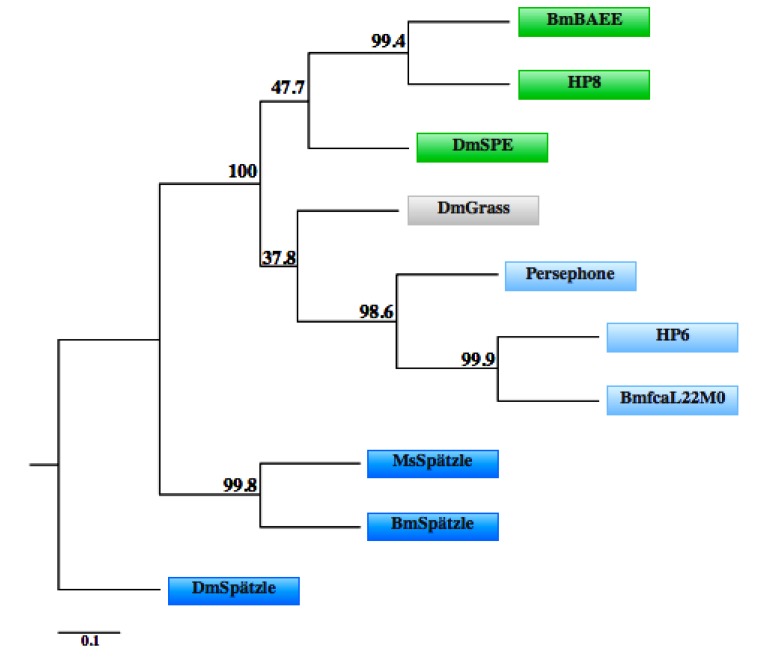
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationships among serine proteases involved in Toll pathway activation. Sequence alignment and tree construction were performed using the amino acid sequence of D. melanogaster (Dm) Grass (Q86PB3), SPE (NP_651168.1), Persephone (Q9VWU1) and Spätzle (NP_524526.1); M. sexta (Ms) HP6 (AAV91004.1), HP8 (AAV91006.1) and Spätzle (ACU68553.1); and B. mori (Bm) fcaL22M01 (AK384444), BAEE (H9J6N1), and Spätzle (NM_001114594). Bm serine proteases were identified by TBLASTN [120] analysis the Bm genome for homologs of Ms serine proteases. The roles of these Bm proteins in Toll pathway activation have not been shown experimentally. One thousand bootstrap repetitions were performed to estimate the reliability of the tree; the percent values obtained are indicated on the nodes. Sequence alignment was performed using Clustal Omega [121,122] bootstrapping analysis, matrix calculation, matrix transformation were conducted by the Fitch-Margoliash method and the combination of the 1,000 resulting trees was identified using the Seqboot, Protdist, Fitch and Consense programs within the Phylip phylogenetic analysis package [123]. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using Phylodendron software version 0.8d, by D.G. Gilbert [124]. The phylogenetic relationships observed are consistent with those previously published [116,119]. Colored boxes for each protein match those presented in Figure 1.