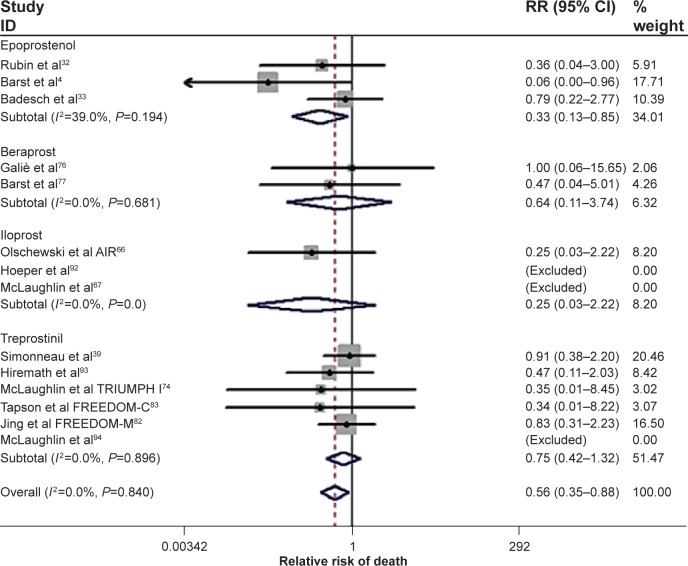
Figure 1.
Forest plot of randomized clinical trials utilizing prostanoid therapies: All cause mortality. Cumulative relative risk (RR) estimate of death in active treatment groups was compared with that in control groups, excluding non-event trials. No heterogeneity was found. Fixed effect model for combined effect size was adopted.
Notes: Data points to the left of the solid line favor the prostanoid treatments, while data points to the right of the solid line favor placebo. Overall relative risk of death with active therapy was 0.56 (95% confidence interval 0.35–0.88, P=0.01). Springer and European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 70, 2013, 13–21, Prostanoid therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: a meta-analysis of survival outcomes, Zheng Y, Yang T, Chen G, et al, Figure 2, © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2013, with kind permission from Springer Science and Business Media.8
Abbreviations: RR, relative risk; CI, confidence interval; AIR, Aerosolized Iloprost Randomized study; TRIUMPH, TReprostinil sodium Inhalation Used in the Management of Pulmonary arterial Hypertension.