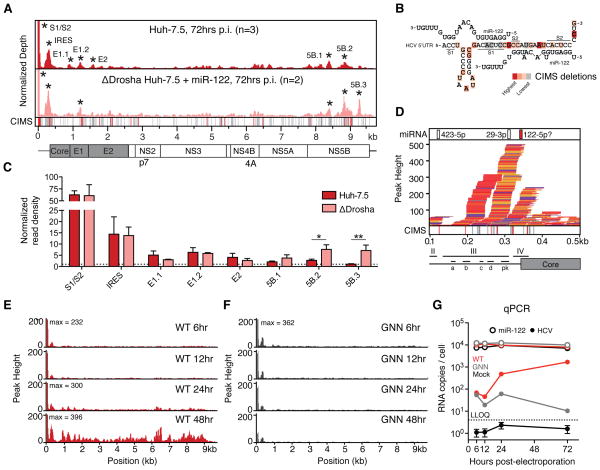
Figure 1.
Argonaute binding maps on HCV RNA. (A) Mock-subtracted binding map of Ago-CLIP reads across HCV genomic RNA in WT or ΔDrosha Huh-7.5 cells. Data were normalized to total cellular and virus read depth for comparison. Significant peaks per track are named by location and indicated by asterisks. Bottom CIMS track shows location of all deletions (gray) and statistically significant CIMS deletions (red) from the WT track. (B) Ago binding in significant peaks from WT Huh-7.5 cells in (A) shown as normalized read densities calculated per dataset. Data were normalized to background read density of non-peak regions (dashed line). Asterisks, **P<0.01, *P<0.05, Student’s t-test. Error bars, ±SD. (C) Schematic of a miR-122 binding model to S1 and S2 highlighting locations of CIMS deletions. (D) Zoom in view of Ago binding from WT cells in (A) across the viral IRES into the coding sequence. IRES domains (II–IV), associated stemloops (a–d) and the pseudoknot (pk) region are indicated. Upper track displays seeds for the top 50 miRNA seeds, previously proposed miR-122 binding (Pang et al., 2012) highlighted in red. (E–F) Ago binding timecourse of WT (E) and replication deficient (GNN) (F) HCV post-electroporation (n=2). (G) Absolute qPCR measurements of miR-122 and HCV RNA levels at indicated time points post electroporation (n=3). Replication-deficient J6/JFH1-GNN and mock controls are shown. Dashed line indicates lower limit of quantitation. Error bars, ±SD. See also Figure S3.