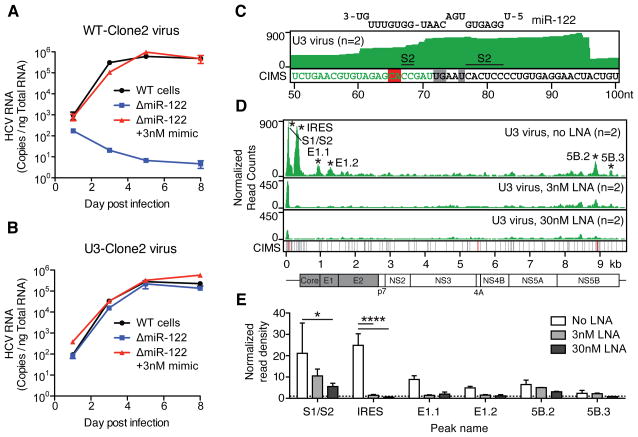
Figure 2.
An HCV mutant resistant to miR-122 antagonism engages Ago and miR-122. (A–B) Timecourse qPCR measurements of WT-Clone2 virus (A) or U3-Clone2 virus (B) in WT cells or in ΔmiR-122 cells with or without 3nM miR-122 supplementation. Error bars, ±SD. (C) Ago binding map (top track) and CIMS locations (bottom track) across the U3 virus 5′UTR corresponding to miR-122 binding at S2. Relevant CIMS deletions are shown in gray (not significant) and red (significant). U3 snoRNA sequence is shown in green. (D) Ago binding map across the U3 virus genome after treatment with increasing doses of LNA122. Significant peaks are named by location and indicated by asterisks. Bottom CIMS track shows location of all deletions (gray) and significant CIMS deletions (red) for the untreated dataset. (E) Ago binding in significant peaks from untreated U3 datasets in (D) shown as normalized read densities calculated per dataset. ****P<0.0001, *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA with bonferroni correction. Error bars, ±SD.