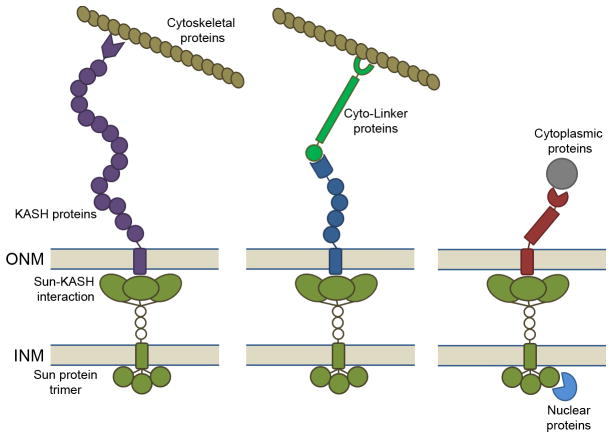
Figure 1. Schematic overview of SUN-KASH interactions.
SUN domain protein trimers form a binding pocket for KASH domain proteins in the perinuclear space. Given that KASH proteins homo-typically oligomerize in an unknown stoichiometry upon SUN domain trimer, KASH proteins are simplified as monomers in this model. Through SUN-KASH luminal coupling, KASH proteins can directly interact with cytoskeletal proteins such as actin (Left). The interactions of KASH proteins and cytoskeletal proteins can be mediated by cyto-linker proteins such as plectin (Middle) or microtubule motor proteins. In addition to the cytoskeletal proteins, KASH proteins are known to bind to diverse cytoplasmic proteins while SUN proteins interact with nuclear proteins likely via the nuclear domain of SUN proteins (Right). The structure of nuclear domain of SUN proteins is remains poorly characterized.