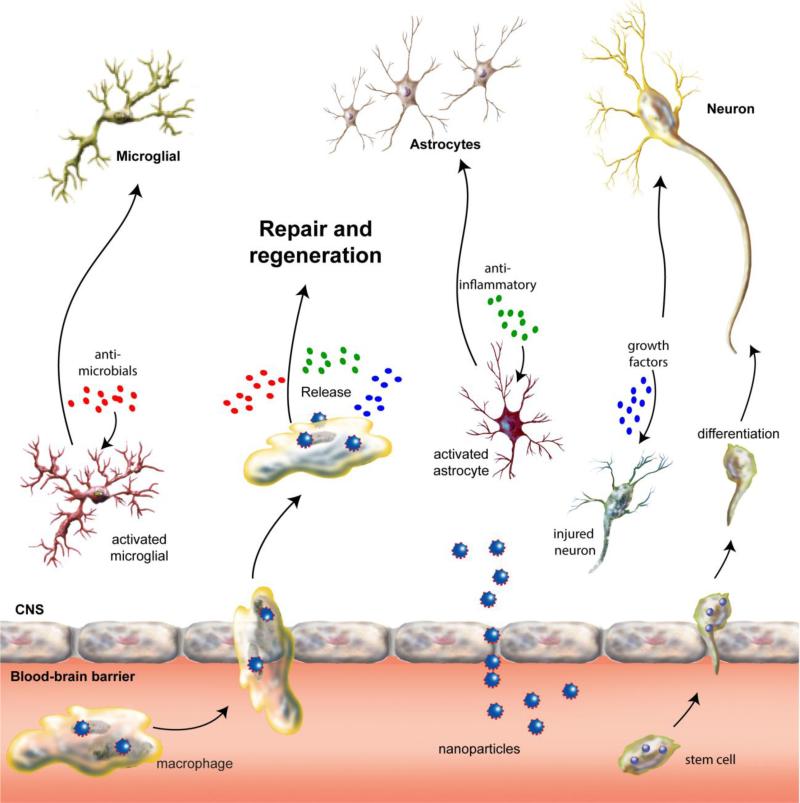
Figure 2. Pathogenesis and nanomedicine treatment of neuroinfectious diseases.
Disease in the CNS is caused, in largest measure, by genetic, degenerative, immune and infectious events. This results in neuronal injury or death, astroglial and microglial activation, or infection with consequent secretion of inflammatory neurotoxic mediators. Nanomedicines can directly cross the blood-brain barrier, affect physiological response barrier function or be carried within circulating immunocytes (monocyte/macrophages and lymphocytes) and stem cells. Once inside the brain, they release their cargo and affect ongoing disease processes leading to clearance of microbial infections, neuronal repair and/or anti-inflammatory responses leading to restoration of glial homeostasis.