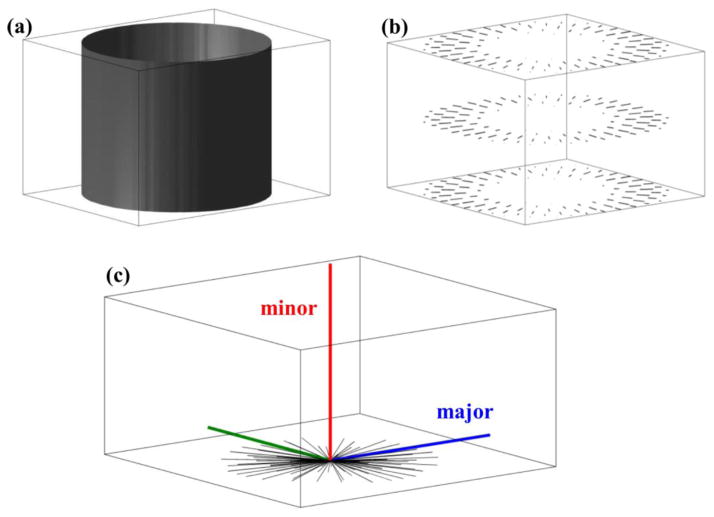
Figure 3.
(a) A synthetic image of a solid cylinder was constructed for illustrating properties of the structure tensor. Here only the surface of the cylinder is shown. (b) A subset of image intensity gradient vectors corresponding to (a) are shown. (c) Structure tensor eigenvectors (red, blue, and green) are shown together with the population of gradient vectors (black). The structure tensor eigenvector that corresponds to the minor eigenvalue (red) is parallel to the cylinder axis of symmetry. The two other eigenvectors correspond to eigenvalues equal in magnitude, and therefore assignment of the major eigenvector is arbitrary for this axially symmetric structure.