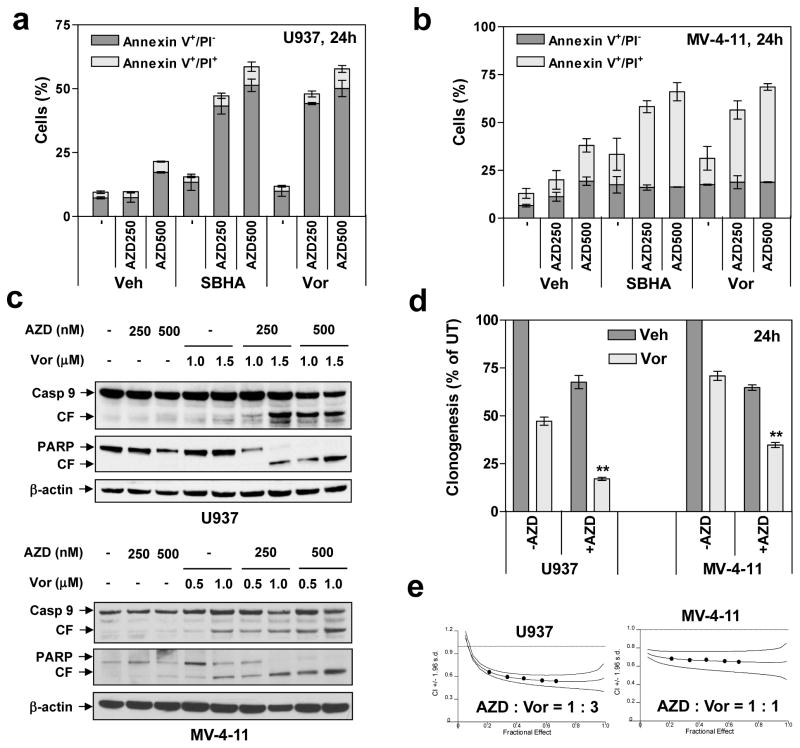
Figure 2. AZD1775 interacts synergistically with HDACIs to induce apoptosis in p53-deficient leukemia cells.
(a–b) U937 (p53-null) and MV4-11 (p53mut, FLT-ITD) cells were exposed to AZD1775 (nM) +/− 1.5μM Vorinostat or 15 μM SBHA for 24 h, after which the percentage of Annexin V+/PI− (early apoptosis) and Annexin V+/PI+ (late apoptosis) was determined by flow cytometry. (c) Alternatively, Western blot analysis was performed to detect cleavage of caspase-9 and PARP. CF = cleaved fragment. (d) After 24 h-exposure to AZD1775 (U937, 500 nM; MV4-11, 250 nM) +/− Vorinostat (U937, 1.5 μM; MV4-11, 0.5 μM), a soft-agar assay was performed to assess colony formation capacity (** P < 0.01). (e) Cells were exposed (24 h) to varying concentrations of AZD1775 and Vorinostat alone and in combination at a fixed ratio. At the end of this period, the percentage of Annexin V+ cells was determined for each condition, and Median Dose-Effect analysis was then employed to characterize the nature of the interaction between these agents. Combination Index (C.I.) values less than 1.0 denote a synergistic interaction. The results are representative for three separate experiments.