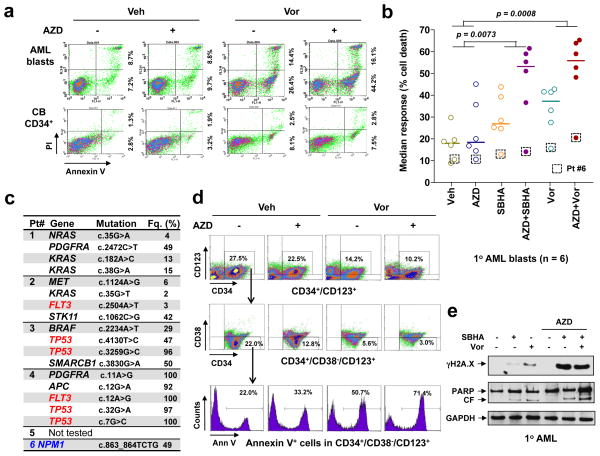
Figure 7. The AZD1775/Vorinostat regimen is active against primary AML cells, including the primitive CD34+/CD38−/CD123+ population, but displays minimal toxicity towards normal CD34+ cells.
(a) Primary blasts from a patient with AML (top) and normal CB CD34+ cells (bottom) were exposed to 250 nM AZD1775 +/− 1.5 μM Vorinostat for 24 h, after which cells were stained with Annexin-V/PI and analyzed by flow-cytometry. Values indicate the percentage of Annexin V+/PI− and Annexin V+/PI+ cells in a total of 10,000 cells analyzed for each condition. (b) Parallel experiments were carried out with six AML primary samples. Median response was analyzed based on the percentage of cell death measured by DiOC6/7AAD double staining and flow cytometry. Squares highlight the weakly-responding sample expressing only the NPM1 mutation (patient #6; see panel c). P values were determined by One-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer Multiple Comparisons Test. (c) In five of these six AML patient samples, NGS was conducted to define genetic abnormalities using the Cancer Hotspot Panel. Fq. = frequency of the mutations. (d) Bone marrow mononuclear cells from a primary AML sample were stained with CD132-APC, CD38-PerCP, CD34-PE, and Annexin-V-FITC, after which the percentage of apoptosis was determined in the primitive CD34+/CD38−/CD123+ population. (e) Western blot analysis was performed to monitor γH2A.X levels and PARP degradation in one representative primary responding sample.