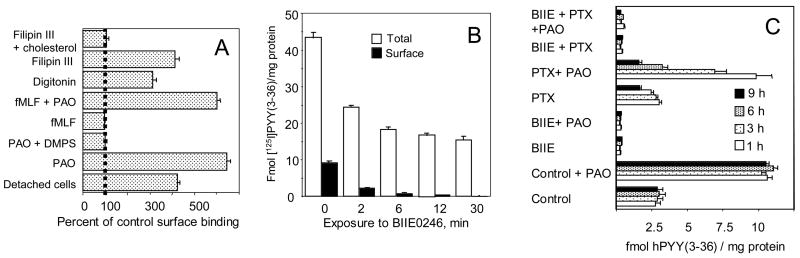
Fig. 2. Compartmentalization of CHO cell Y2 receptors and inactivation by antagonist BIIE0246.
A Activation of the masked Y2 surface sites by various agents and treatments. Non-disruptive cell detachment was done by silicone rubber, followed by sedimentation at 100 x g, resuspension and incubation with the labeled agonist. Phenylarsine oxide (PAO) and DMPS were used at 30 μM, fMLP at 100 μM, digitonin at 6 μM, and filipin 3 at 3 μM (without or with 30 μM cholesteryl hemisuccinate). Digitonin at 6 μM exposed, without cell detachment, about 4 fmol [35S]GTP-γ-S sites/100,000 cells, while 30 μM PAO or detachment by rubber exposed less than 1 fmol/100,000 cells. Total [35S]GTP-γ-S sites (as measured with particulates) were about 20 fmol/100,000 cells.
B Kinetics of inactivation of CHO cell receptors by Y2 antagonist BIIE0246. The cell monolayers were exposed to 100 nM of the antagonist for 2, 6, 12 and 30 min, followed by several cycles of washing and then by labeling of total (particulate) and surface (monolayer) receptors for 12 min at 37 °C with 50 pM [125I]PYY(3-36) (the later in the presence of 30 μM PAO, to expose the masked sites). With total particulates from this experiment, the Kdiss values in pM (with Bmax, fmol/mg protein, in parenthesis) were 438 ± 88 (506 ± 39) without the antagonist, and 545 ± 60 (21 ± 12) after 100 nM of the antagonist.
C Compared inactivation of surface Y2 sites by Y2 antagonist BIIE0246 (10 nM) and PTX (10 ng/ml). The inhibitors were applied to CHO cell monolayers separately or together for the indicated periods in the cell culture medium. After washing, the monolayers were labeled with [125I]PYY(3-36) for 20 min at 23 °C without or with 30 μM phenylarsine oxide, extracted with cold acid saline, and the extracts counted. The results are expressed in fmol per mg total cell protein.