FIG 3.
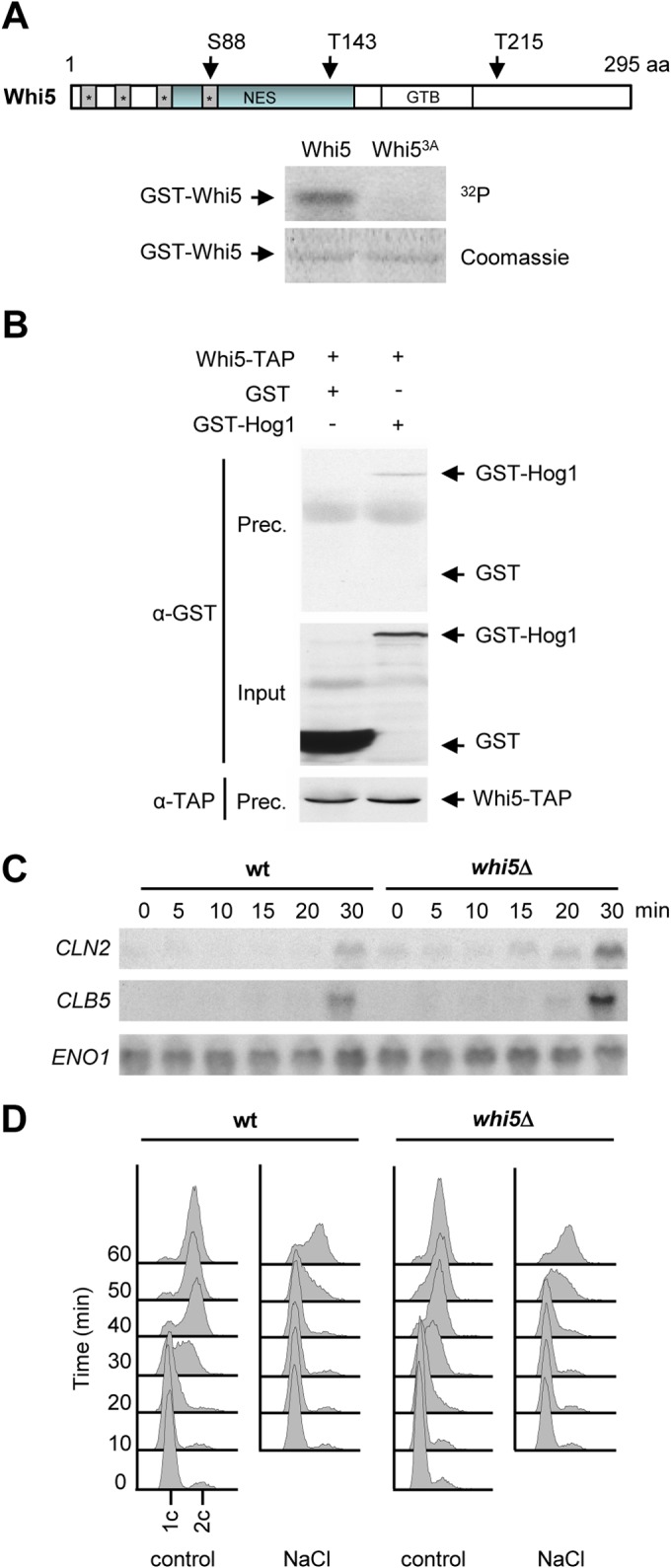
Whi5 is targeted by Hog1 upon osmostress. (A) Mutation of Whi5 Ser88, Thr143, and Thr215 abolishes Hog1 phosphorylation in vitro. Bacterially expressed GST-Whi5 or GST-Whi53A was employed as a substrate in an in vitro kinase assay. Hog1 and the constitutively activated Pbs2EE allele were incubated in kinase buffer containing ATP. Whi5 or Whi53A was then added in the presence of radioactive ATP. Phosphorylated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography (top). GST-tagged proteins were detected by staining with Coomassie brilliant blue (bottom). A schematic representation of Whi5 is shown at the top, indicating the location of the three residues phosphorylated by Hog1. The gray boxes denote predicted nuclear localization signals. The blue boxes denote the nuclear export signal (NES), and the GTB box denotes the G1/S transcription factor binding motif. aa, amino acids. (B) Whi5 and Hog1 interact in vivo. Cells expressing Whi5-TAP with either GST-Hog1 or GST alone were exposed to 0.4 M NaCl for 10 min, and anti-TAP antibody was used to immunoprecipitate Whi5. Precipitated proteins (Prec.) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GST and anti-TAP antibodies as probes. The input represents 2.5% of the immunoprecipitated protein. (C) Absence of Whi5 does not rescue the delay in G1 cyclin transcription induced by osmostress. Wild-type (wt) and whi5Δ mutant cells were synchronized with α-factor and released into 0.4 M NaCl. RNA extracted from samples taken at the time points indicated was analyzed by Northern blotting with probes specific for CLN2 and CLB5 mRNAs. ENO1 mRNA expression was analyzed as a loading control. (D) DNA replication delay induced by osmostress is not dependent on Whi5. Wild-type and whi5Δ mutant cells were synchronized in G1 with α-factor and released into YPD medium (control) or 0.4 M NaCl. DNA content was measured by flow cytometry every 10 min after release.
